Figure 1.
The CasDrop system enables liquid condensation of transcriptional regulators at target loci.
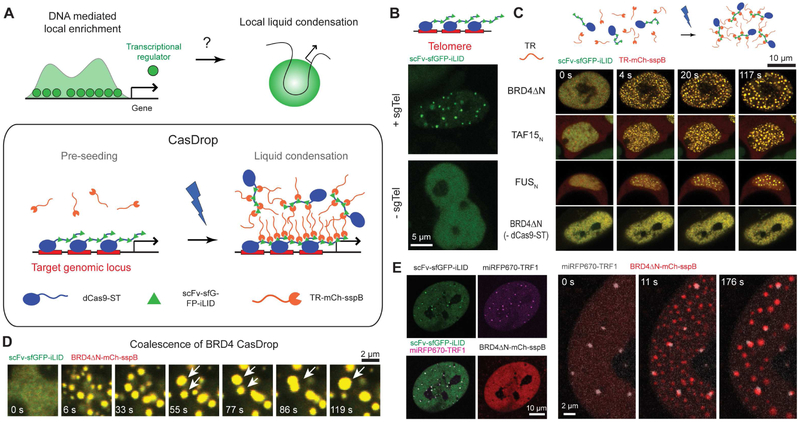
(A) Transcriptional regulators (TRs) are often enriched at regulatory DNA elements near genes and may facilitate local liquid-liquid phase separation. The CasDrop system is designed to function similarly yet with added genome-targeting programmability and optogenetic controllability. The modular components of the CasDrop include dCas9-ST, scFv-sfGFP-iLID and TR-mch-sspB.
(B) Pre-seeding at telomeres in a HEK293 cell by expressing dCas9-ST, scFv-sfGFP-iLID and sgRNA for telomeres. In the absence of the telomere-targeting sgRNA, punctate fluorescence signals are not observed.
(C) HEK293 cells expressing dCas9-ST, scFv-sfGFP-iLID and mch-sspB fused to different transcriptional regulators (TR) are activated with blue light. A control without expressing the dCas9-ST scaffold shows no clustering.
(D) Time lapse images of BRD4 CasDrop in a HEK293 cell showing rapid condensation followed by frequent coalescence between droplets (white arrowheads).
(E) (Left) Fluorescence images of a NIH3T3 cell expressing dCas9-ST, scFv-sfGFP-iLID, BRD4ΔN-mCh-sspB, miRFP670-TRF1 and sgRNA for telomeres. Images show localization patterns of each construct prior to blue light activation. (Right) Time lapse images of the same cell during blue light illumination.
See also Figure S1