Figure 2.
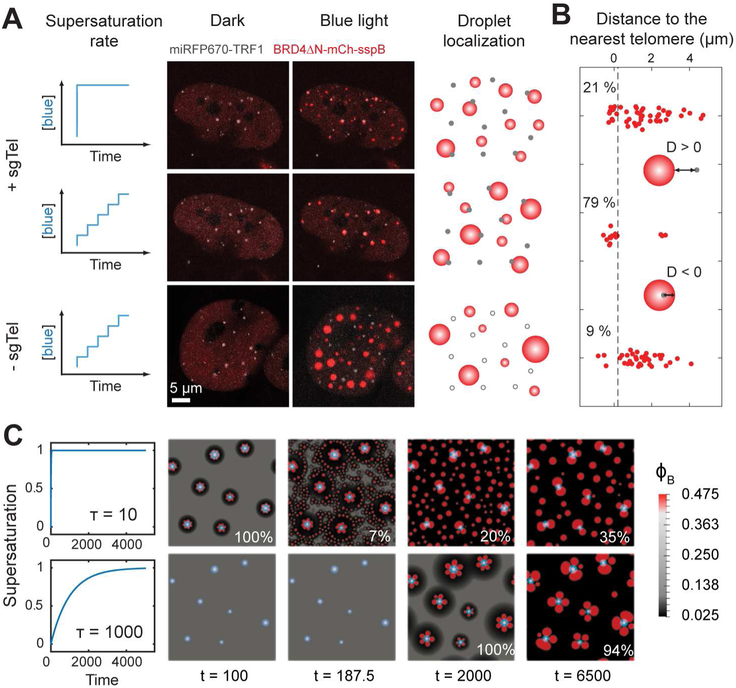
The effects of pre-seeding and activation protocol on the localization pattern of BRD4 CasDrop.
(A) Two different activation protocols are applied to the same NIH3T3 cell expressing dCas9-ST, scFv-sfGFP-iLID, BRD4ΔN-mCh-sspB, miRFP670-TRF1 and sgRNA for telomeres. Fluorescence images of the cell before and after activation protocols are shown. When the ramping protocol is applied on a cell without telomere-targeting sgRNA, assembled droplets exhibited apparently random droplet localization irrespective of telomeres.
(B) For each BRD4 droplet, a distance from the droplet boundary to the nearest telomere is measured. Each red dot represents a single droplet. Fractions of droplets whose distances to the nearest telomere are smaller than 0.2 μm (black dashed line) are given in percentage.
(C) Simulations of our mechanical droplet exclusion model demonstrating that during CasDrop nucleation and growth in the presence of pre-seed sites (white circles denote stiff seed cores, light blue halos denote surrounding regions of enhanced concentration, φA) targeted droplet localization improves with decreasing activation rate. Rapid and slow activation protocols are shown in the upper and lower rows, respectively, with time increasing from left to right. Fractions of droplets overlapping with a pre-seed site at the final time shown are given in percentage.
See also Supplementary Videos 1-2