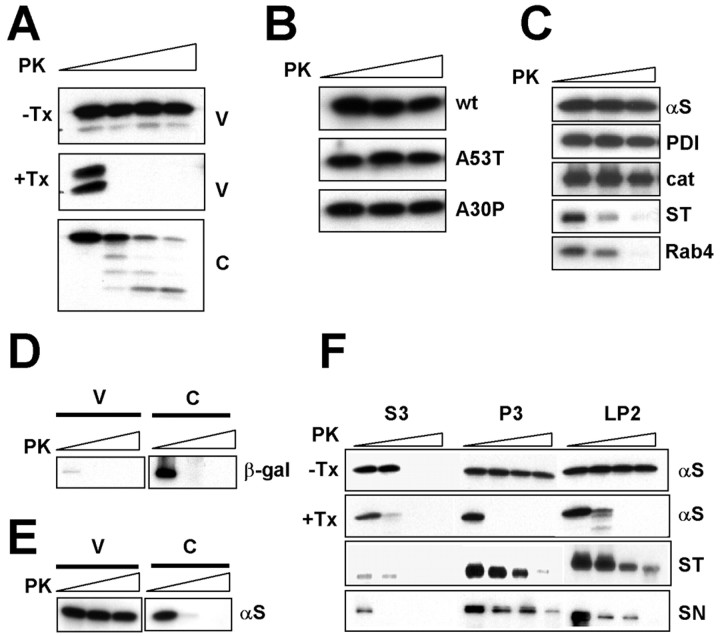
Figure 2.
Vesicular α-syn is not accessible to protease digestion. A, PK resistance of vesicular α-syn. V and C prepared from differentiated SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with different concentrations of PK. Note that detergent-mediated solubilization of membrane (1% Triton X-100) eliminates PK resistance of vesicular α-syn. B, PK resistance of mutant α-syn in vesicles. Microsomal vesicles were prepared from differentiated SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing wild type (wt) or mutants and incubated with different concentrations of PK (0, 0.1 and 1 μg/ml). C, PK digestion of other vesicular proteins. Microsomal vesicles from SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with PK. Concentrations of PK: 0, 0.1 and 1 μg/ml. D, PK sensitivity of β-galactosidase (β-gal). V and C from SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing β-galactosidase were treated with 0, 0.1, and 1 μg/ml PK. E, PK sensitivity of neuronal endogenous α-syn. Vesicular and cytosolic fractions were isolated from rat cortical neurons and treated with PK. F, PK sensitivity of brain α-syn. Microsomal vesicles (P3), crude synaptic vesicles (LP2), and cytosol (S3) were prepared from rat brain homogenate and subjected to PK digestion. +Tx, With 1% Triton X-100; -Tx, without Triton X-100; αS, α-syn; cat, catalase; ST, synaptotagmin 1; SN, synapsin 1.