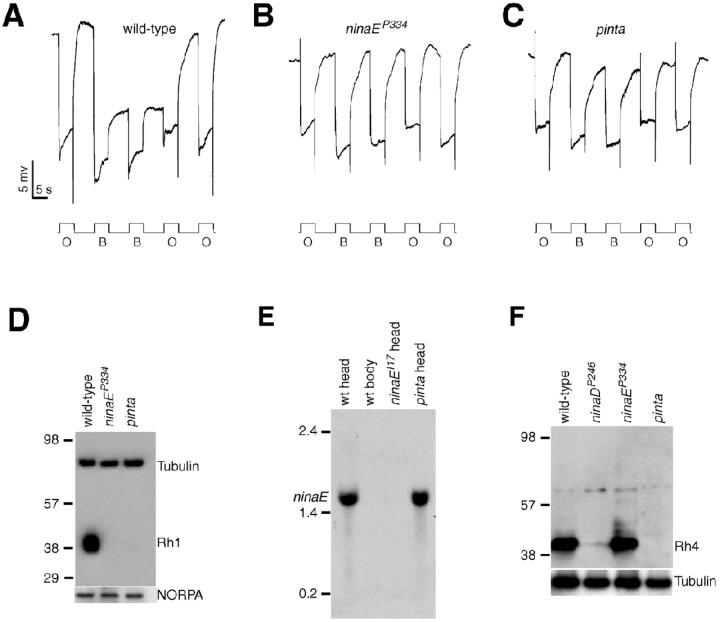
Figure 1.
Rhodopsin biosynthesis and PDA defects in pinta. A-C, ERG paradigm that elicits a PDA in wild type, but not mutants, with reduced Rh1 levels. Flies (<2 d after eclosion) were dark-adapted for 1 min and subsequently exposed to 5 s pulses of orange light (O) or blue light (B) interspersed by 7 s, as indicated. A PDA is induced in wild type by blue light and terminated by orange light. A, Wild type (w1118); B, ninaEP334; C, pinta. D, Rh1 is reduced in ninaEP334 and pinta flies. Western blots containing extracts prepared from fly heads (2 d after eclosion) were probed with anti-Rh1 and anti-tubulin antibodies. Molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the left. A parallel blot containing the same extracts was probed with anti-NORPA antibodies. E, ninaE mRNA levels assayed by Northern blot analysis. Each lane contained 20 μg of total RNA. Similar signals in each lane were obtained after reprobing with a ribosomal protein 49 probe (data not shown). Single-stranded RNA markers are indicated to the left. wt, Wild type. F, Western blot showing Rh4 expression was reduced in pinta heads. The Western blot was probed with anti-Rh4 antibodies. The same blot was reprobed with anti-tubulin antibodies.