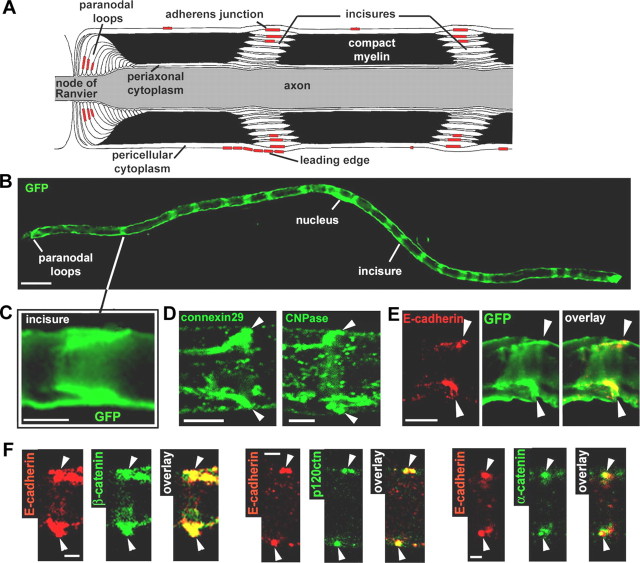
Figure 1.
AJ and architecture of the myelinated Schwann cell. A, Longitudinal view of a myelinated Schwann cell showing the different compartments and the respective location of the AJs. B, Myelinated Schwann cell infected with an adenovirus expressing GFP and showing repeated bands of cytoplasm corresponding to the location of incisures. Scale bar, 50 μm. C, GFP-filled incisure showing the pair of angled cytoplasmic regions representing one incisure as depicted in A. Scale bar, 10 μm. D, Immunostaining of connexin29 (left) and CNPase (right) showing their enrichment in an incisure (arrowheads). Scale bar, 5 μm. E, Pair of E-cadherin clusters (red) that localize at the outer edge of a GFP-filled incisure (arrowheads). Scale bar, 10 μm. F, Coimmunostaining of E-cadherin (red) and β-catenin, p120ctn, and α-catenin (green) on sciatic nerve samples at 2 months postnatal (arrowheads indicate pairs of E-cadherin clusters). Scale bar, 2.5 μm.