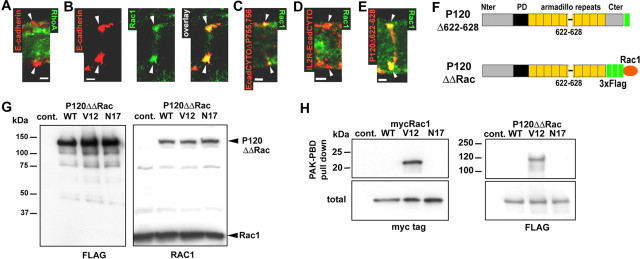
Figure 7.
Rac1 colocalization with AJ correlates with the recruitment of p120ctn to cadherin. A, RhoA (green) does not colocalize with E-cadherin (red) at incisures (arrowheads). Scalebar, 2.5 μm. B, Rac1 (green) partially colocalizes with E-cadherin (red). Scalebar, 2.5 μm. C, IL2R-EcadCYTOΔP755,756 (red) partially colocalizes with Rac1 (green). Scalebar, 2.5 μm. D, IL2R-EcadCYTO (red) does not colocalize with Rac1 (green). Scalebar, 2.5 μm. E, P120Δ622-628 construct (red) colocalizes with Rac1 (green). Scalebar, 2.5 μm. F, The C terminal (Cter) of P120Δ622-628 was fused to a 3xFlag tag and Rac1 wild-type, dominant-active mutant (V12) and dominant-negative mutant (N17) to obtain P120ΔΔRacWT, V12, and N17. G, P120ΔΔRac constructs were expressed in CHO cells and immunoblotted with mouse monoclonal anti-Flag (left) or anti-Rac1 (right) antibodies. Note that anti-Rac1 antibody recognizes both Rac1 and P120ΔΔRac. H, myc-Rac1 (left) and P120ΔΔRac (right) constructs expressed in CHO were subjected to PAK-PBD pull down, and the precipitated proteins were detected by Western blots hybridized with anti-myc and anti-Flag antibodies. A sample of the total amount of protein subjected to precipitation was also processed (total) to show that the same amount of protein was used for each construct. Nter, N terminal; Cont., control.