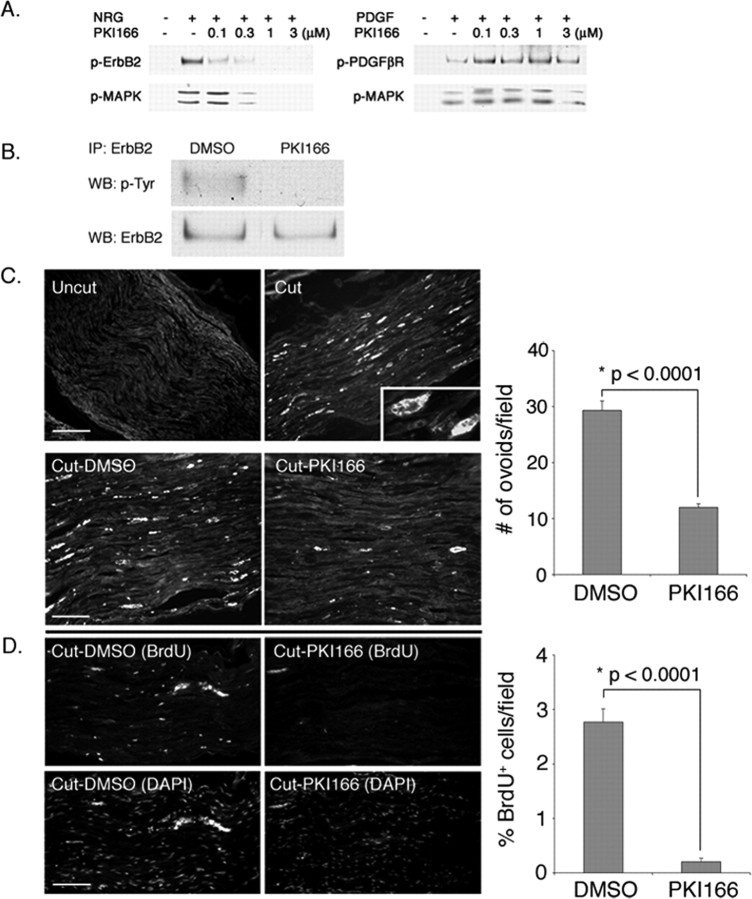
Figure 4.
PKI166 blocks Schwann cell response to nerve injury in vivo. A, PKI166 is a selective inhibitor of erbB2 activation. Primary rat Schwann cells were pretreated with various concentrations of PKI166 for 15 min and then stimulated with neuregulin (NRG) (30 ng/ml) or PDGF (30 ng/ml) for 5 min. Cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation using antibodies to erbB2 or PDGFβR, followed by immunoblotting using antibodies to p-Tyr. Activation of the downstream signaling protein MAPK was determined by immunoblotting using p-MAPK antibody. As indicated, PKI166 inhibits activation of erbB2 and also MAPK in response to neuregulin but has no effect on PDGFβR activation or PDGF-induced signaling events. B, PKI166 inhibits axotomy-induced erbB2 activation in vivo. Thirty minutes before axotomy, rats were injected intraperitoneally with PKI166 or solvent control. One hour after axotomy, distal stump nerves were harvested. Nerve lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibody to erbB2 and immunoblotted with p-Tyr antibody. IP, Immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot. C, Ovoids of myelin are a convenient metric for demyelination. Frozen sections of uncut or axotomized sciatic nerves were immunostained at 2 d after surgery with antibody to MBP. Top, In uncut nerve, the myelinated axons are evenly stained with the antibody. In a cut nerve, more intense staining on spherical clumps of myelin debris (ovoids) is visible. Inset, Higher magnification of an ovoid stained with anti-MBP antibody. Scale bar, 50 μm. Bottom, Ovoid formation is retarded in PKI166-treated animals. Rats were injected with PKI166 or solvent control as in B. After axotomy, rats were treated with a daily injection of PKI166 (Cut-PKI166) or solvent control (Cut-DMSO) for 2 d. Distal nerves were harvested and immunostained for MBP. Scale bar, 30 μm. D, Schwann cell proliferation is blocked in animals treated with PKI166 after nerve injury. Surgery and drug treatments are the same as in B. Schwann cell proliferation in control and axotomized rats was visualized by injecting rats with BrdU at 2 d after axotomy and then immunostaining with anti-BrdU antibody. Bottom panels show Schwann cell nuclei stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 50 μm. Quantifications of the experiments in C and D are shown on the right. The mean values and SEM were calculated from three independent experiments with each experiment containing data obtained from at least 20-30 random fields. Asterisks indicate statistical significance was determined by ANOVA test.