Figure 1.
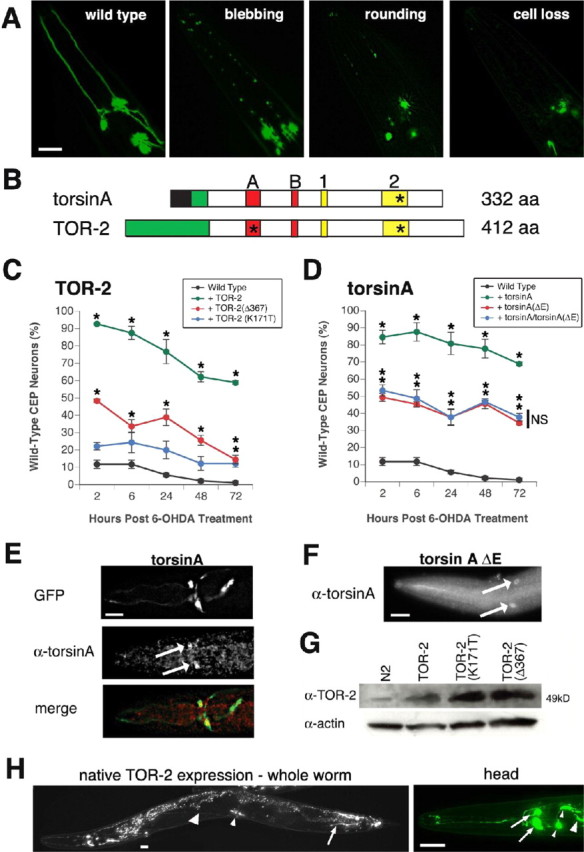
Torsin-mediated protection of C. elegans DA neurons against 6-OHDA. A, Different stages of DA neurodegeneration. From left to right, representative temporally staged images depicting CEP DA neuron morphology of wild type, neuronal process blebbing, process loss and cell body rounding, and cell body loss are shown. Scale bar, 20 μm. B, Schematic representation of torsin domains and mutations. Top, Human torsinA; bottom, C. elegans TOR-2; black region, signal peptide; green region, putative hydrophobic transmembrane domain; A, Walker A domain; B, Walker B domain; 1, sensor 1 domain; 2, sensor 2 domain. The asterisks mark the approximate positions of mutations that were analyzed. Mutations within sensor 2 correspond to the EOTD-associated mutation [torsinA(ΔE302/303)] and the structurally analogous change in worm TOR-2 [TOR-2(Δ367)]. The mutation within the Walker A domain corresponds to an alteration within a conserved ATP-binding site [TOR-2(K171T)]. C, TOR-2 protection against 6-OHDA. After 6-OHDA treatment, worms were examined for the presence of all four wild-type CEP neurons at specific time points: green, TOR-2; blue, TOR-2(K171T); red, TOR-2(Δ367); black, Pdat-1::GFP without TOR-2 overexpression. D, TorsinA protection against 6-OHDA. Green, TorsinA; blue, torsinA/torsinA (ΔE302/303) combination; red, torsinA(ΔE302/303); black, Pdat-1::GFP without torsinA overexpression. Statistical significance between Pdat-1::GFP and each of the six torsin-overexpressing lines was assessed at each time point between all transgenic lines by the ANOVA Bonferroni's test (*p < 0.05; NS, not significant). Error bars in C and D indicate SEM between independent experiments. E, Immunolocalization of torsinA in DA neurons in human torsin-overexpressing worms. Top, Two CEP neurons marked by GFP fluorescence; middle, torsinA antibody immunostaining in CEP cell bodies (arrows); bottom, merge of top and middle images. Scale bar, 20 μm. F, Immunolocalization of torsinA in torsinA(ΔE302/303)-overexpressing worms in CEP cell bodies (arrows). Scale bar, 20 μm. The GFP and merge images are not shown because they were reminiscent of those in Figure 1 E. G, Western analysis to verify TOR-2 overexpression in TOR-2-overexpressing worms. Actin was probed for each sample as a loading control. H, Native TOR-2 expression pattern in transgenic worms in which GFP is driven by a genomic region upstream and inclusive of the C. elegans tor-2 gene. Left, Entire worm depicting expression in the AVE neurons (large arrowhead), vulva muscle cells (small arrowhead), and PVW neurons (arrow); gut autofluorescence is also observed throughout the intestinal tract. Right, Close-up of the anterior head region, showing expression in the M1 pharyngeal neuron (large arrowhead), the AW class of neurons (2 small arrowheads), and the AVE interneurons (2 arrows). Expression in DA neurons is not observed. Scale bar, 20 μm.
