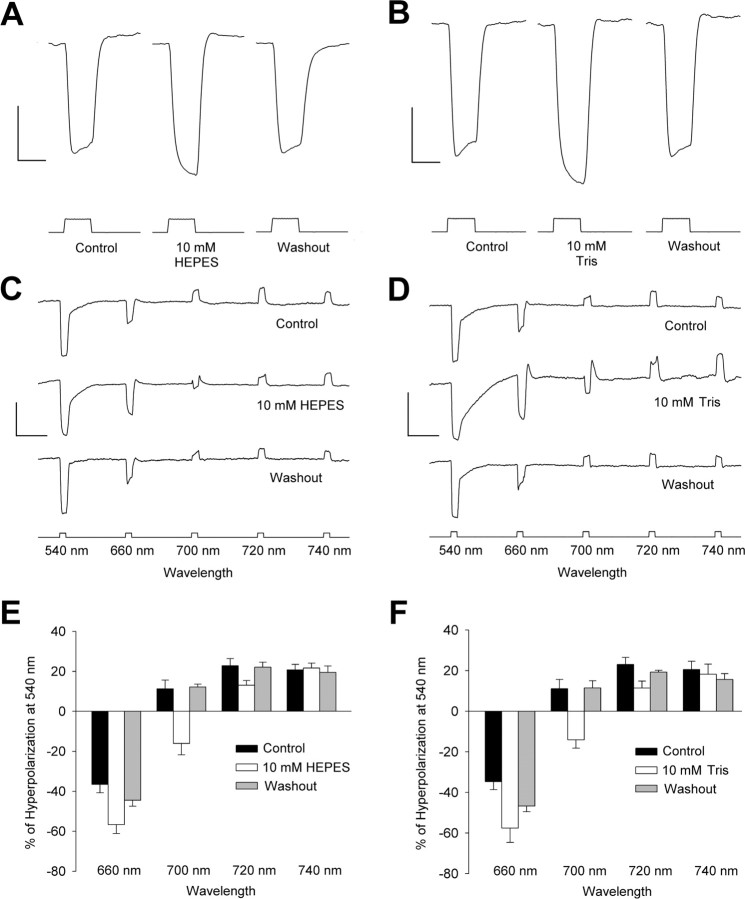
Figure 1.
Increased pH buffering reduces the feedback response of horizontal cells. A, B, Representative recordings from six different H1 HCs in response to full-field illumination in a retina before (left trace), during (middle trace), and after (right trace) 10 mm HEPES (A) and Tris (B) were added to the bicarbonate-buffered bathing medium. Both HEPES and Tris abolished the rollback in the waveform of the HC response. Calibration: 10 mV, 500 ms. C, D, Representative recordings from six different H2 HCs in response to equal quanta 540, 660, and 700 nm stimuli in a retina before (top trace), during (middle trace), and after (bottom trace) treatment with 10 mm HEPES (C) or Tris (D). Both HEPES and Tris blocked the depolarizing response to 700 nm stimuli and increased the amplitude of the hyperpolarizing response to 660 nm stimuli. The amplitude of the response to 540 nm was not affected by either HEPES or Tris. Calibration: 20 mV, 2.5 s. E, F, Mean response to 660 and 700 nm stimuli in all cells studied expressed as a percentage of the response to 540 nm stimuli. Both 10 mm HEPES (E) and Tris (F) increased the mean response to 660 nm stimuli and inverted the response to 700 nm stimuli.