Figure 6.
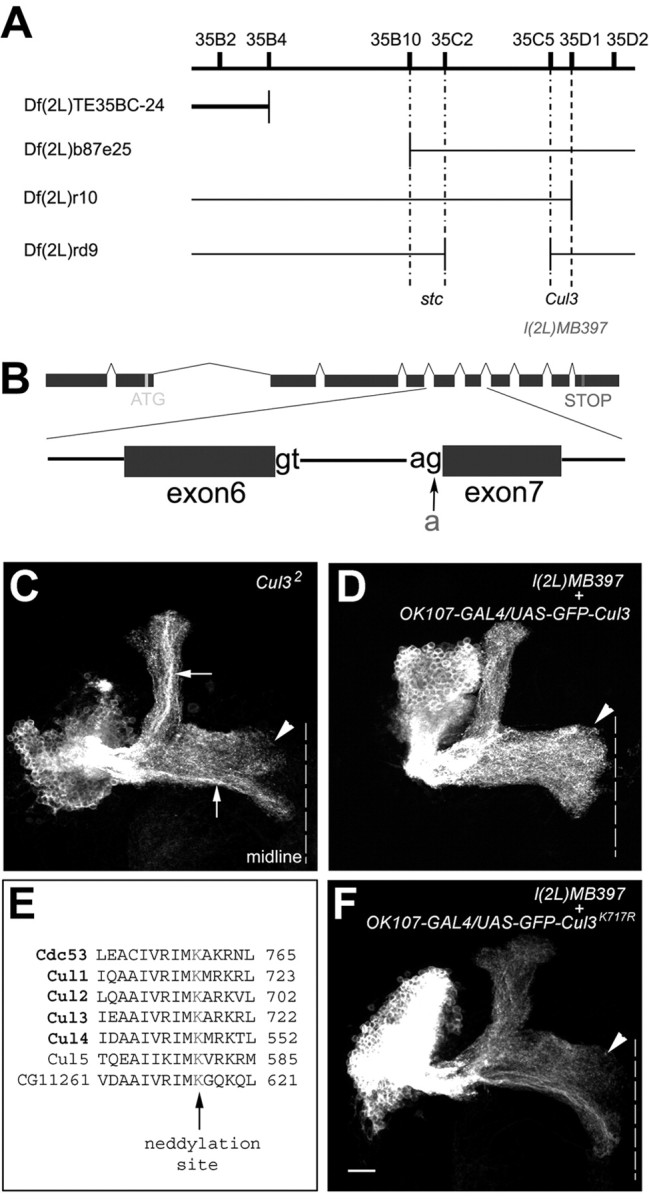
l(2L)MB397 carries a splicing mutation in Cul3, and the conserved neddylation site is essential for Cul3 activity. A, l(2L)MB397 fails to complement with the deficiency line whose deficiency region is indicated by the gap in the thick line but complemented with the deficiency lines whose deficiency regions are indicated by gaps in thin lines. Additional complementation tests assign l(2L)MB397 to the Cul3 complementation group. B, l(2L)MB397 carries a g-to-a mutation at the acceptor site of the intron between exon 6 and exon 7 of Cul3. C, The Cul32 mutant Nb clone shows terminal morphogenetic defects in the γ and β′ lobes (arrowhead). Also note the dense axon fascicles within the α and β lobes (arrows). D, All of the medial lobes are fully extended (arrowhead) in the l(2L)MB397 mutant Nb clone in which GFP-tagged wild-type Cul3 is autonomously expressed. E, Partial sequence alignment among yeast Cul1 (Cdc53) and six Drosophila cullin proteins. Consensus neddylation sites are highlighted in red. F, The terminal defects of the γ and β′ lobes (arrowhead) remain in the l(2L)MB397 mutant Nb clones that autonomously express GFP-tagged Cul3K717R. Genotype: C, hs-FLP,UAS-mCD8-GFP/X;Cul32,FRT40A/tubP-GAL80,FRT40A;GAL4-OK107/+; D, hs-FLP/UAS-GFP-Cul3;l(2L)MB397,UAS-mCD8-GFP,FRT40A/tubP-GAL80,FRT40A;GAL4-OK107/+; F, hs-FLP/X;l(2L)MB397,UAS-mCD8-GFP,FRT40A/tubP-GAL80,FRT40A;UAS-GFP-Cul3K717R/+;GAL4-OK107/+.
