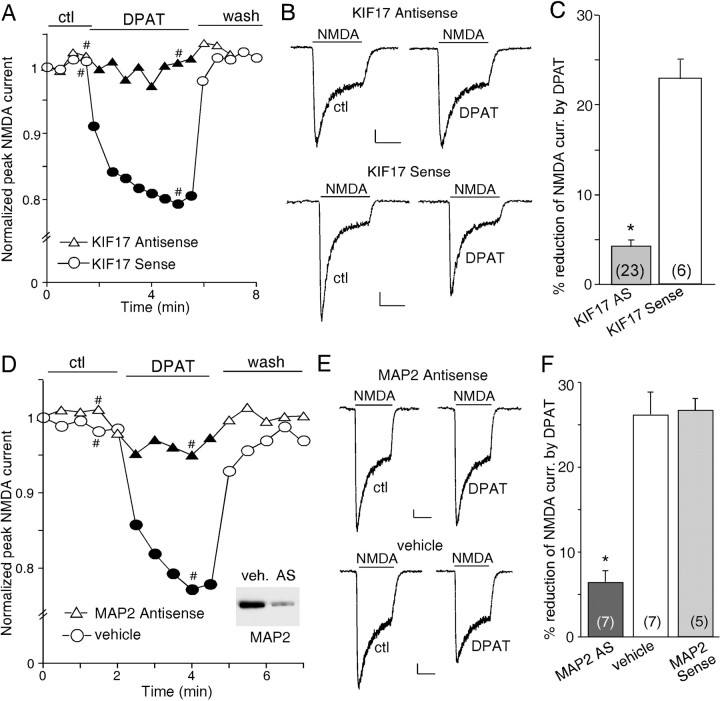
Figure 4.
The 5-HT1A modulation of NMDAR currents involves the transport of NR2B-containing vesicles along microtubules by the kinesin motor protein KIF17 and requires the microtubule-binding protein MAP2.A, Plot of peak NMDAR currents as a function of time and agonist [8-OH-DPAT (DPAT), 20 μm] application in neurons treated with KIF17 antisense or sense oligonucleotides. B, Representative current traces taken from the records used to construct A (at time points denoted by #). Calibration: 100 pA, 1 s. C, Cumulative data (mean ± SEM) showing the percentage reduction of NMDAR currents by 8-OH-DPAT in a sample of cultured neurons treated with KIF17 antisense or sense oligonucleotides. D, Plot of peak NMDAR currents as a function of time and 8-OH-DPAT (40 μm) application in neurons treated with MAP2 antisense oligonucleotides or vehicle control. Inset, Western blot analysis of MAP2 expression in cultured PFC neurons treated with vehicle (veh.) or MAP2 antisense oligonucleotides (AS). E, Representative current traces taken from the records used to construct D (at time points denoted by #). Calibration: 100 pA, 1 s. F, Cumulative data (mean ± SEM) showing the percentage reduction of NMDAR currents by 8-OH-DPAT in a sample of cultured neurons treated with MAP2 antisense oligonucleotides, vehicle control, or MAP2 sense oligonucleotides. The number of cells tested in each condition is shown in each bar (C, F). *p < 0.005, ANOVA. ctl, Control.