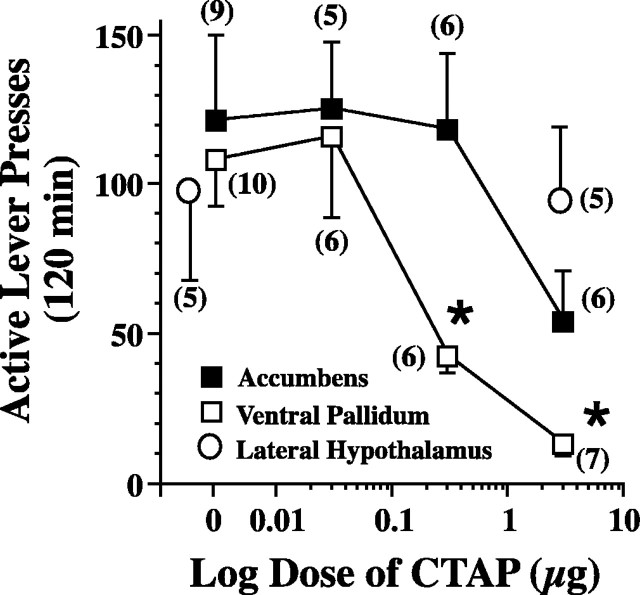
Figure 1.
μ Receptors in the ventral pallidum critically regulate cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking in rats extinguished from cocaine self-administration. After reaching extinction criterion (on the extinction trial the day before the reinstatement trial: ventral pallidum group, 15 ± 3 active lever presses; nucleus accumbens group, 9 ± 3), rats were microinjected into the ventral pallidum, nucleus accumbens, or lateral hypothalamus with CTAP or saline vehicle just before administering a cocaine-priming injection (10 mg · kg-1 · ml-1, i.p.). Data were evaluated using a mixed-regression analysis, and each rat received a maximum of two reinstatement trials (ventral pallidum, F(3,8) = 13.88, p = 0.002; nucleus accumbens, F(3,11) = 1.82, p = 0.202), except the lateral hypothalamus data, which were evaluated using a paired Student's t test (p = 0.687). All data are shown as mean ± SEM active lever presses. The number of determinations at each dose is shown in parentheses. *p < 0.05 compared with saline microinjection within each brain nucleus.