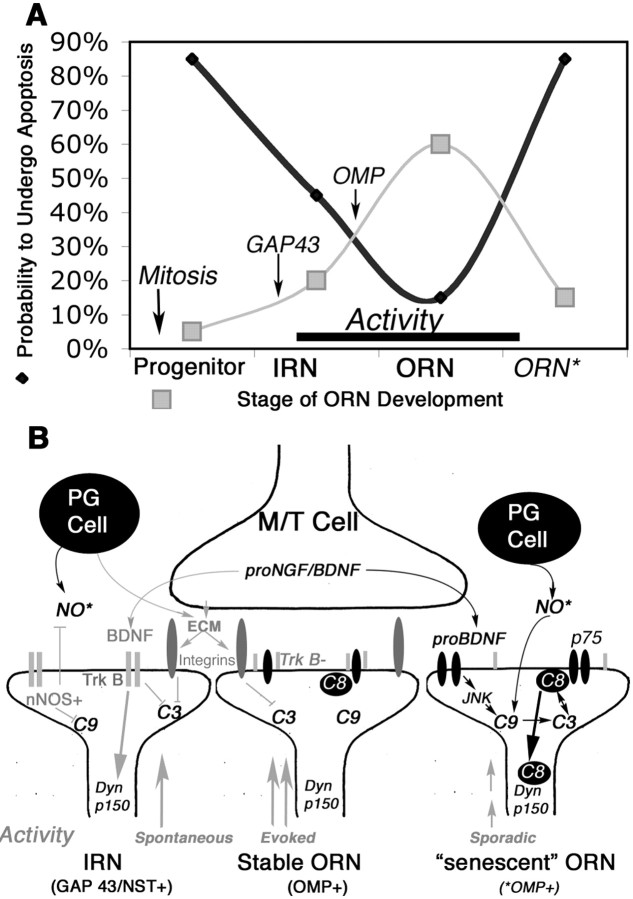
Figure 9.
Opposing prosurvival and proapoptosis pathways in ORNs as they shift in a developmental state. A, Summary indicating the representative frequencies of OE-based ORN populations and the frequency with which ORNs of different stages undergo apoptosis in the OE. Newly generated and molecularly senescent ORNs are the most vulnerable, and immature and mature ORNs stabilized by activity are the most resistant. Markers of populations used in this study (GAP43, OMP) are also indicated. B, Pathways of apoptotic vulnerability at the synapse and how they may inhibit, or lead to, caspase-8 translocation to dynactin. Prosurvival signals are in gray, and proapoptotic signals are in black. Dyn p150, p150Glued, Dynactin subunit; ECM, extracellular matrix; JNK, Jun kinase; M/T, mitral/tufted cells; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; NO*, nitric oxide; p75, low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor, p75; PG, periglomerular cells; TrkB, kinase active; TrkB-, truncated TrkB.