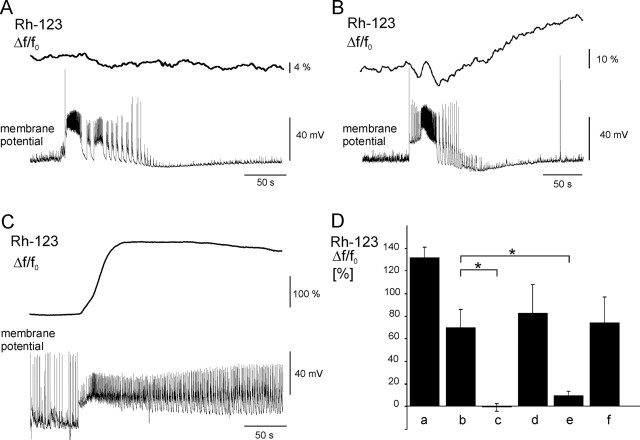
Figure 5.
Dependence of ΔΨm changes on mitochondrial Ca2+ ion cycling and opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. A, Representative trace of Rh-123 fluorescence changes during an SLE in the presence of Ru360 (180 μm) in the pipette solution. Inhibition of the mitochondrial Ca2+ ion uniporter prevented elevation of cytosolic Rh-123 fluorescence. B, Representative trace of Rh-123 fluorescence changes during an SLE in the presence of the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ ion exchanger inhibitor CGP-37157 (15 μm) in the pipette solution. CGP-37157 decreased SLE-associated Rh-123 elevation. C, Representative trace of Rh-123 fluorescence elevation in the presence of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore inhibitor cyclosporin A in the perfusion. Note the lengthening of the CLADP. D, Comparison of the effects of mitochondrial Ca2+ ion cycling and mitochondrial permeability transition pore inhibitors as well as protonophores on the mitochondrial depolarization during SLEs. Application of a protonophore (a; n = 3 cells), SLE-associated elevations (b; n = 30 SLEs from 12 cells), SLE-associated changes in the presence of Ru360 (c; n = 19 SLEs from 9 cells), application of a protonophore in the presence of Ru360 (d; n = 6 cells), SLE-associated changes in the presence of CGP-37157 (e; n = 12 SLEs from 5 cells), and SLE-associated elevations in the presence of cyclosporin A (f; n = 10 SLEs from 5 cells). Asterisks indicate significant differences. Error bars represent SEM.