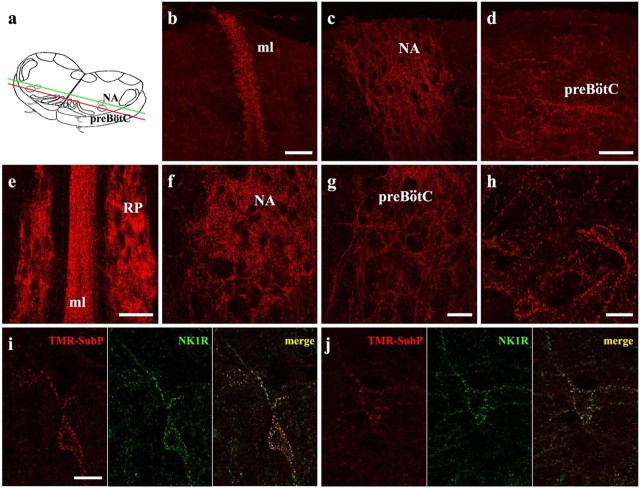
Figure 2.
Internalization of TMR-SubP in living medullary slice preparations. a, Schematic drawing of medullary slices used for TMR-SubP internalization experiments. The green and red lines delineate the coronal plane from which images b and c (green) and d (red) were taken. b-d, TMR-SubP internalization along the coronal plane at the midline (ml; b), more laterally at the nucleus ambiguus (NA; c), and more ventrolaterally at the preBötC (d). The top part of the figures corresponds to the rostral surface of the slice. e-h, TMR-SubP internalization in medullary slices along the transverse plane. A 5 min application of TMR-SubP (500 nm) results in robust internalization into neurons located in the midline, raphe pallidus (RP; e), nucleus ambiguus (f), and preBötC (g, h). i, j, Colocalization of TMR-SubP fluorescence (red) and NK1R immunolabeling (green) in preBötC neurons. Fine and punctate staining for both NK1R and TMR-SubP is present in preBötC neurons. Note the high level of colocalization (yellow puncta) in the cell body and dendrites of preBötC neurons. Scale bars: (in b, d, e, g), b-g, 50 μm; (in h, i) h-j, 20 μm.