Figure 1.
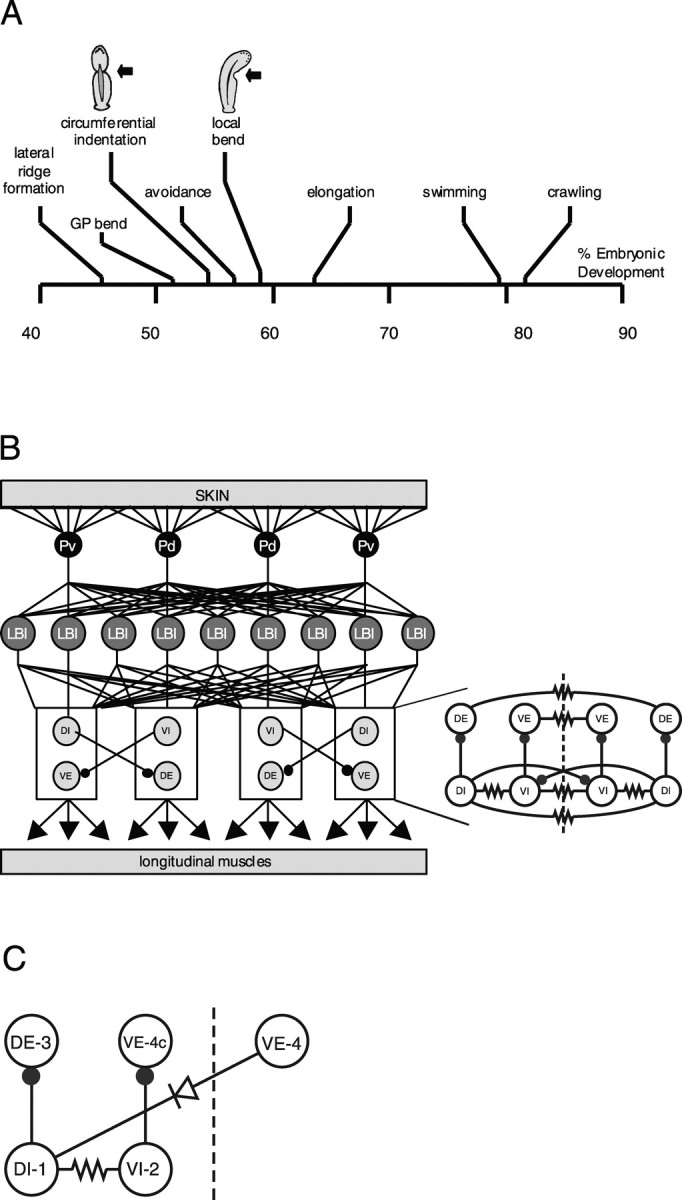
Development of behaviors and LB circuit of the leech. A, Time line for development of behavior in Hirudo embryos. Time is measured as a percentage of total ED (% ED). GP, Germinal plate. Drawings of CI and LB illustrate the behaviors. Moderate pressure produces CI between 55 and 60% ED and LB after 60% ED. Data are modified from Reynolds et al. (1998b). B, Left, Diagram of the LB circuit drawn as though a leech was cut along the ventral midline and stretched out. The four P mechanosensory neurons that innervate the ventral (Pv) and dorsal (Pd) regions of the body wall are shown in black, LBIs are shown in dark gray, and inhibitory (DI and VI) and excitatory (DE and VE) motor neurons innervating longitudinal muscle are shown in light gray. The only known inhibitory connections in the circuit (represented by black circles at the end of the lines connecting the neurons) are made between motor neurons. Data are adapted from Kristan et al. (2000). Right, Detailed longitudinal motor neuron circuit. Each segmental ganglion contains 16 bilateral pairs of longitudinal motor neurons interconnected centrally by both chemical (filled circles) and electrical (resistor symbol) synapses. The central connections for 12 of these pairs are summarized here. The dashed line indicates the ventral midline. Each circle represents a class of two to four neurons that form the same pattern of connections. Class abbreviations indicate the region of longitudinal muscle innervated (e.g., dorsal vs ventral) and the neuronal polarity (i.e., excitatory vs inhibitory). DI, Dorsal inhibitors; DE, dorsal excitors; VI, ventral inhibitors; VE, ventral excitors. On each side of the ganglion, there are two DIs, four DEs, three VIs, and three VEs. All neurons within each class are electrically coupled; their connections have been left out for graphic clarity. C, Reduced longitudinal motor neuron circuit. Each circle represents an individual neuron from the classes shown in B. Most leech motor neurons project contralaterally, whereas cell VE-4 projects ipsilaterally. Therefore, the soma of cell VE-4 is contralateral to the somata of other motor neurons that have the same motor fields, and we designate it VE-4c. Filled circle, Inhibitory chemical synapse; resistor, nonrectifying electrical synapse; diode, rectifying electrical synapse.
