Figure 5.
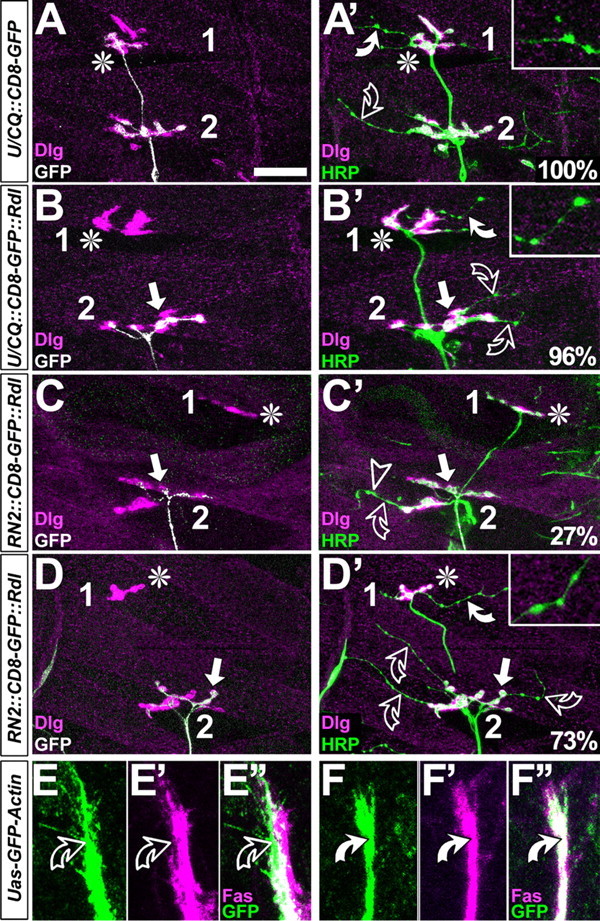
FasciclinII might not act merely as a homophilic adhesion factor. A-D′, Dorsal muscle fields of embryos at the late first and early second instar larval stage; symbols are as in Figure 4 and stainings are indicated at the bottom left. In control hemisegments, CD8-GFP-labeled U neurons grow to the most dorsal muscle (asterisk in A), as does the entire nerve (HRP in A′). Whereas motor neuronal type 1 terminals display large boutons and are double-labeled with Dlg and HRP (white color in A′), terminals of type 2 modulatory VUM neurons are slim and lack Dlg [throughout this figure, white curved arrows and closeups show type 2 terminals on DA1/DO1 muscles; open curved arrows show type 2 terminals on DA2/DO2; for terminal classification, compare Landgraf et al. (2003)]. If U neurons are stalled (arrow in B, B′), terminals of remaining ISN type 1 terminals are almost always present (asterisk in B), and VUM neurons are seen in most dorsal positions in 96% of these cases. If aCC/RP2 neurons are stalled (white arrows in C-D′), nearly all ISN neurons coarrest (Fig 4 A′,D,E), but in 30% of cases U neurons escape (asterisks in C-D′); in these cases, VUM neurons are absent on dorsal muscles in 27% (C′) and present in the remaining 73% (D′). E-F″, Growth cones and axons of aCC/RP2 (green in C-C″; RN2::GFP-actin) mostly show low levels of FasciclinII (magenta) on exposed surfaces (curved open arrows), whereas GFP-Actin expressed in U neurons (green in D-D″; U/CQ::GFP-actin) is always congruent with high levels of FasciclinII (curved white arrows). Scale bar: A-B′, 25 μm; C-D″, 8 μm.
