Figure 5.
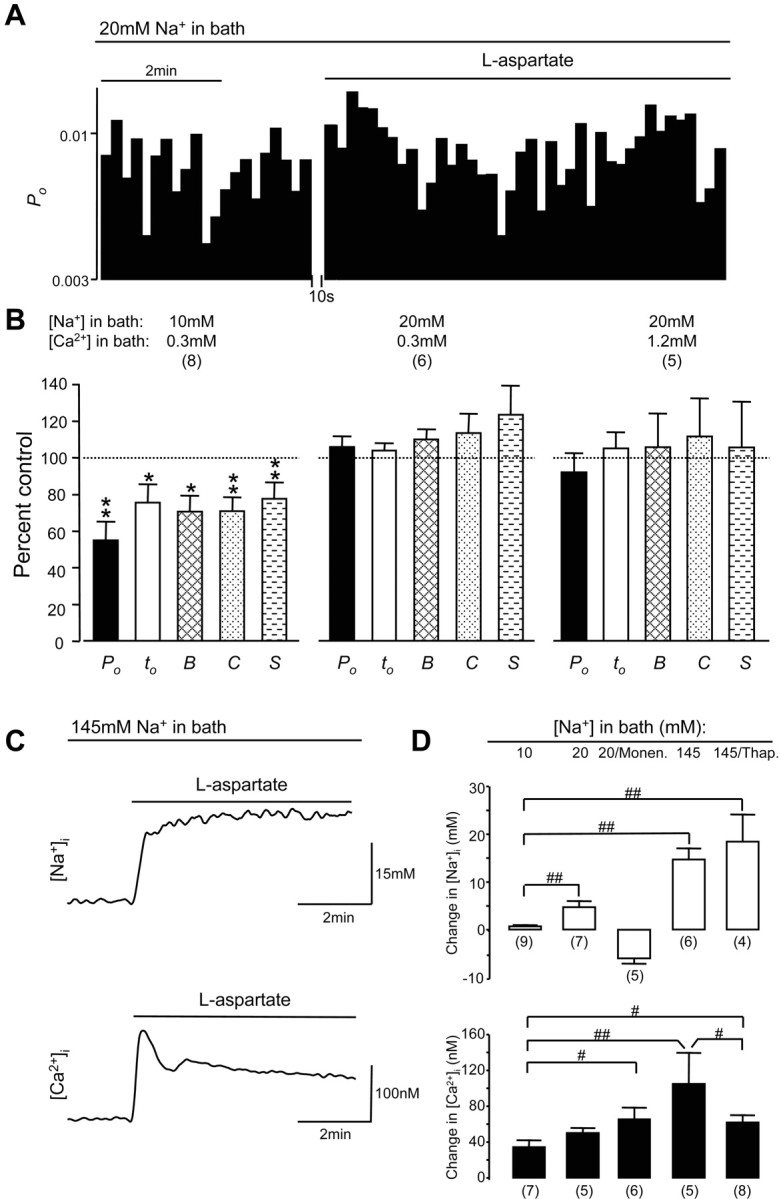
Ca2+ influx-induced downregulation of NMDA channel gating during activation of remote NMDA receptors could be overcome by a modest Na+ influx. A, An example of NMDA channel open probability (Po; bin, 10 sec) recorded from neurons bathed with an extracellular solution containing 20 mm Na+ and 0.3 mm Ca2+. B, Summarized data (mean ± SEM) outlining the effects of remote NMDA receptor activation produced by the bath application of l-aspartate on Po, mean open time (to), burst (B), cluster (C), and supercluster (S) lengths of NMDA channels recorded from neurons bathed with an extracellular solution containing 10 mm Na+ and 0.3 mm Ca2+ or 20 mm Na+ and 0.3 mm Ca2+ or 20 mm Na+ and 1.2 mm Ca2+. Values in parentheses indicate the number of patches tested. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Wilcoxon test). C, Examples of traces of [Na+]i (top) and [Ca2+]i (bottom) recorded in the soma region of neurons bathed with the extracellular solution containing 0.3 mm Ca2+ and 145 mm Na+ before and during l-aspartate (500 μm) application. D, Summarized data indicating changes (mean ± SEM) in [Na+]i (top) and [Ca2+]i (bottom) induced by the activation of NMDA receptors in neurons bathed with extracellular solutions containing 0.3 mm Ca2+ and 10, 20, or 145 mm Na+ in the absence and presence of monensin (10 μm) or Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin (0.1 μm); # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney test) in a comparison between groups as indicated. Values in parentheses indicate the number of neurons tested.
