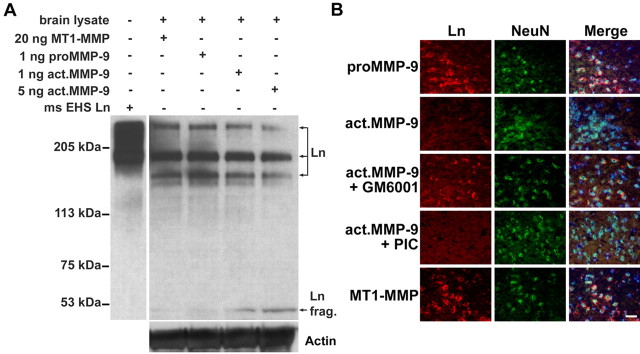
Figure 4.
Exogenous MMP-9 degrades lamininin the extracellular matrix protein of mouse brain. A, Western blot with a pan-Ln polyclonal antibody reveals degradation of laminin (especially the 360 and 170 kDa subunits) to a 51 kDa fragment (frag.) in brain lysates treated with activated MMP-9 but not with latent proMMP-9 or catalytic MT1-MMP (50 μg of total protein per lane). Purified mouse Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm laminin (ms EHS Ln) served as a molecular marker for laminin immunoblotting. The membrane was reblotted with anti-actin antibody to ensure equal protein loading in each lane. B, Ex vivo degradation of neuronal laminin by exogenous MMP-9 in mouse-brain sections. Double immunolabeling of laminin by pan-Ln polyclonal antibody (Ln; red) and neurons with NeuN antibody (green) reveals that activated MMP-9 degraded neuronal laminin. A broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor, GM6001, significantly reduced laminin degradation, whereas a non-MMP PIC did not. Latent proMMP-9 or catalytic MT1-MMP could not degrade neuronal laminin. Merged images were counterstained with Hoechst dye to visualize nuclei (blue). Scale bar, 25 μm.