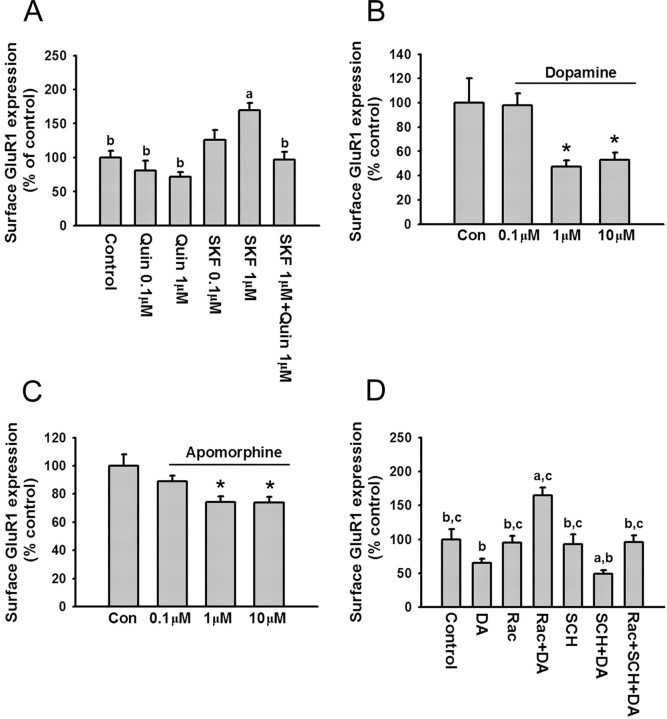
Figure 7.
Dopamine decreases surface GluR1 expression on PFC neurons via D2 receptor activation. A, The D2 agonist quinpirole blocks the increased surface GluR1 expression induced by D1 receptor stimulation. Quantification of surface GluR1 expression in control neurons (medium; 10 min) and neurons treated with quinpirole (0.1 or 1 μm; 10 min), SKF 81297 (0.1 or 1 μm; 10 min), or quinpirole (1 μm) plus SKF (1 μm) (a, p < 0.05 compared with control group; b, p < 0.05 compared with SKF 81297 group; Dunn's test; n = 24-39). B, C, Dopamine and apomorphine decrease surface GluR1 expression. Quantification of cell-surface GluR1 staining in control neurons (medium; 10 min) and neurons treated with DA (0.1, 1, or 10 μm; 10 min; n = 28-43) or apomorphine (0.1, 1, or 10 μm; 10 min; n = 26-31). Both drugs significantly decreased surface GluR1 expression (*p < 0.05; Dunn's test). D, Quantification of cell-surface GluR1 staining in control neurons and neurons treated with raclopride (1 μm), raclopride (1 μm) plus DA (1 μm), SCH 23390 (10 μm), SCH 23390 (10 μm) plus DA (1 μm), and raclopride (1 μm) plus SCH 23390 (10 μm) plus DA (1 μm). Cells were incubated with antagonists for 5 min, and then DA was added for another 10 min (a, p < 0.05 compared with control group; b, p < 0.05 compared with raclopride plus DA group; c, p < 0.05 compared with SCH plus DA group; n = 20-37). Error bars indicate SEM. Quin, Quinpirole; Rac, raclopride; Con, control.