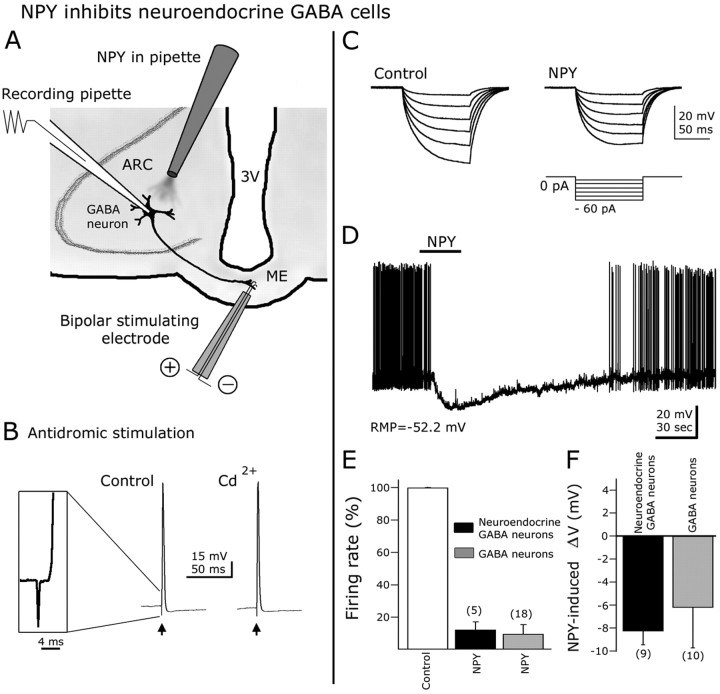
Figure 4.
NPY inhibits ARC neuroendocrine GABAergic neurons. A, Schematic representation of hypothalamic slice preparation used to study neuroendocrine cells. 3V, Third ventricle. B, Antidromic responses (action potentials) were evoked in GFP-expressing cells after median eminence electrical stimulation with a bipolar electrode. The action potentials induced by ME antidromic stimulation persisted in 200 μm CdCl2 in the bath, indicating that these responses were not attributable to transmitter release induced by orthodromic activation of recurrent axon collaterals. Inset shows the spike latency and initial rise of an action potential evoked by ME stimulation. C, In this typical cell, negative current steps (see protocol in the bottom part) were delivered before (control) and during NPY application. A robust reduction in the hyperpolarizing responses after negative current injection was observed in the presence of NPY, consistent with a decrease in whole-cell input resistance. D, In current-clamp conditions, NPY blocked spikes and hyperpolarized ARC neuroendocrine neurons. E, F, NPY-induced reduction in spike frequency and hyperpolarization in neuroendocrine neurons were not significantly different from that of other ARC GABA cells. Error bars indicate SE. The number of cells is shown in parentheses.