Figure 6.
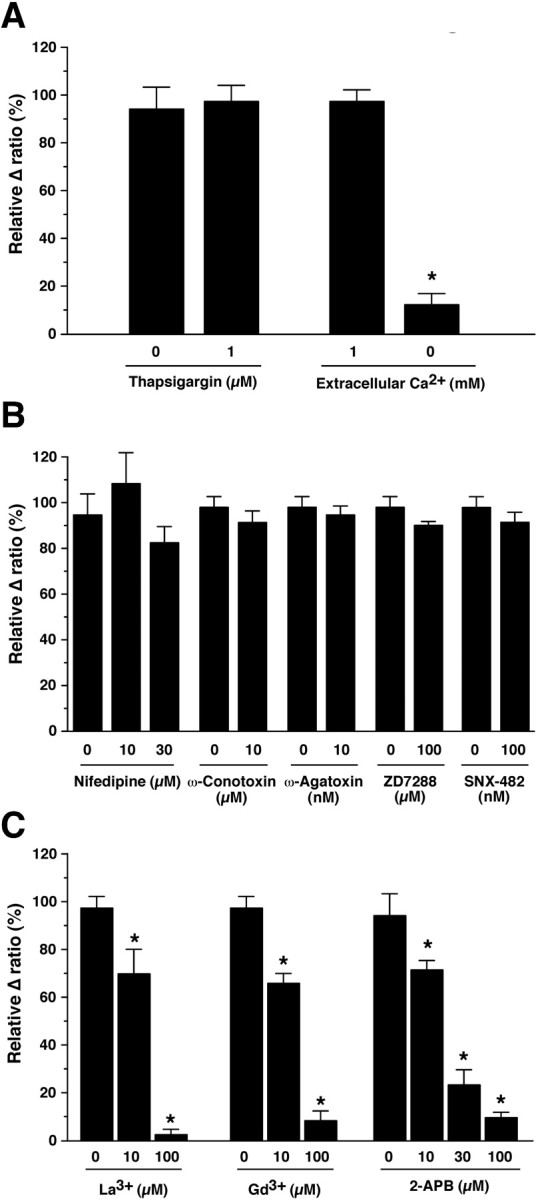
Ca2+ imaging of orexin neurons using brain slices prepared from orexin/YC2.1 mice revealed that CCK-8S activates nonselective cation channels on the orexin neurons. The experiments were performed in the presence of TTX (1 μm). A, CCK-8S-induced increase in [Ca2+]i was significantly inhibited by removal of extracellular calcium (n = 9) but was not inhibited by thapsigargin (1 μm) treatment (n = 13). B, The effect of voltage-dependent calcium channel blockers on CCK-8S-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. Nifedipine (10 μm, n = 5; 30 μm, n = 8), ω-conotoxin (10 μm, n = 7), ω-agatoxin (10 nm, n = 5), ZD7288 (100 μm, n = 6), and SNX-482 (100 nm, n = 8) did not inhibit CCK-8S-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. C, The effect of nonselective cation channel blockers on CCK-8S-induced increase in [Ca2+]i. La3+ (10 μm, n = 8; 100 μm, n = 7), Gd3+ (10 μm, n = 7; 100 μm, n = 6), and 2-APB (10 μm, n = 5; 30 μm, n = 6; 100 μm, n = 5) inhibited CCK-8S-induced increase in [Ca2+]i in a concentration-dependent manner. Data are normalized by Δ ratio obtained by CCK-8S (30 nm) application before experiments. Drugs were dissolved in the extracellular solution and were applied by bath application for 5 min before the experiments. Thapsigargin, nifedipine, and 2-APB were dissolved in ethanol and were compared with vehicle control (0.1% ethanol). Values are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.
