Figure 1.
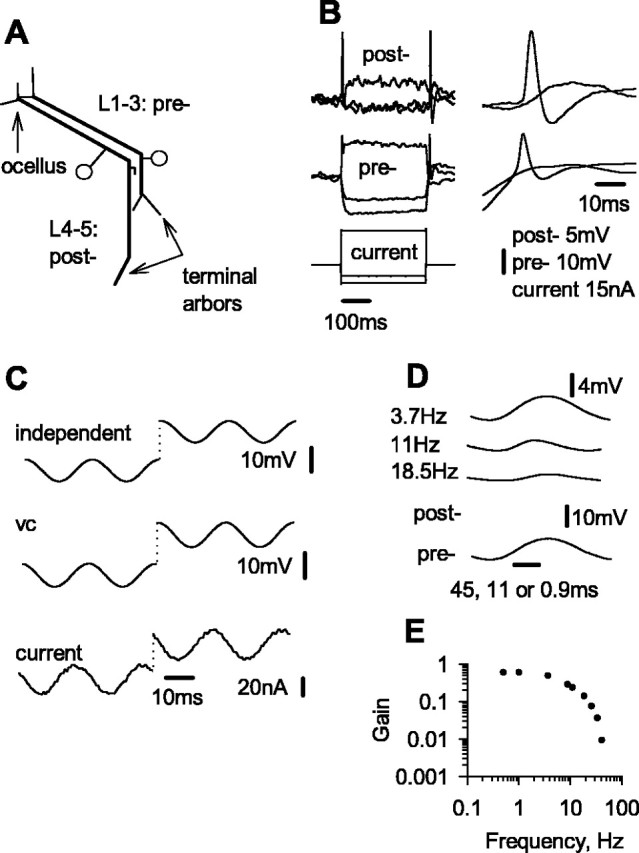
General features of the excitatory synapse between L-neurons. A, Summary of the morphologies of an L1-3 neuron and an L4-5 neuron. Each neuron has an axon with one arbor in the lateral ocellus and another in the brain. Discrete anatomical contacts of the excitatory synapses are made in the ocellar tract from the axon of L1-3 onto fine, stubby processes that project from the axon of L4-5. One process is represented near the bend in the ocellar tract. B, Graded transmission across the synapse, demonstrated by using one electrode to inject current pulses into the presynaptic neuron while separate electrodes recorded the membrane potentials of the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons. At dark resting potential, the synapse releases neurotransmitter tonically so that both depolarizing and hyperpolarizing changes in potential are conveyed (left). Sudden depolarizing potentials in both neurons are enhanced by rebound spikes, which are graded in amplitude (details are shown in the right panels). C, A two-electrode voltage clamp allows good control of membrane potential over a range of voltages. The current-injecting and voltage-clamp electrodes were placed 200 μm apart in the axon of an L-neuron in the ocellar tract, while an independent recording electrode was placed in the same axon in the ocellar tact, ∼200 μm from the origin of the nerve. Recordings are shown from two 50 Hz sine waves, the first oscillating about dark resting potential and the second depolarized by 15 mV. D, E, Frequency-dependent transmission across the synapse. A voltage clamp-controlled presynaptic potential, which was held at a mean 15 mV depolarized from dark resting potential and driven with sine waves of various frequencies. Averages of postsynaptic potential over 10 cycles are shown for three different frequencies, with different time scales, so that the recordings of presynaptic potential superimpose. E, Plots of synaptic gain (averages of 10 cycles; peak-to-trough postsynaptic/presynaptic) against frequency. pre-, Presynaptic; post-, postsynaptic; vc, voltage command.
