Figure 3.
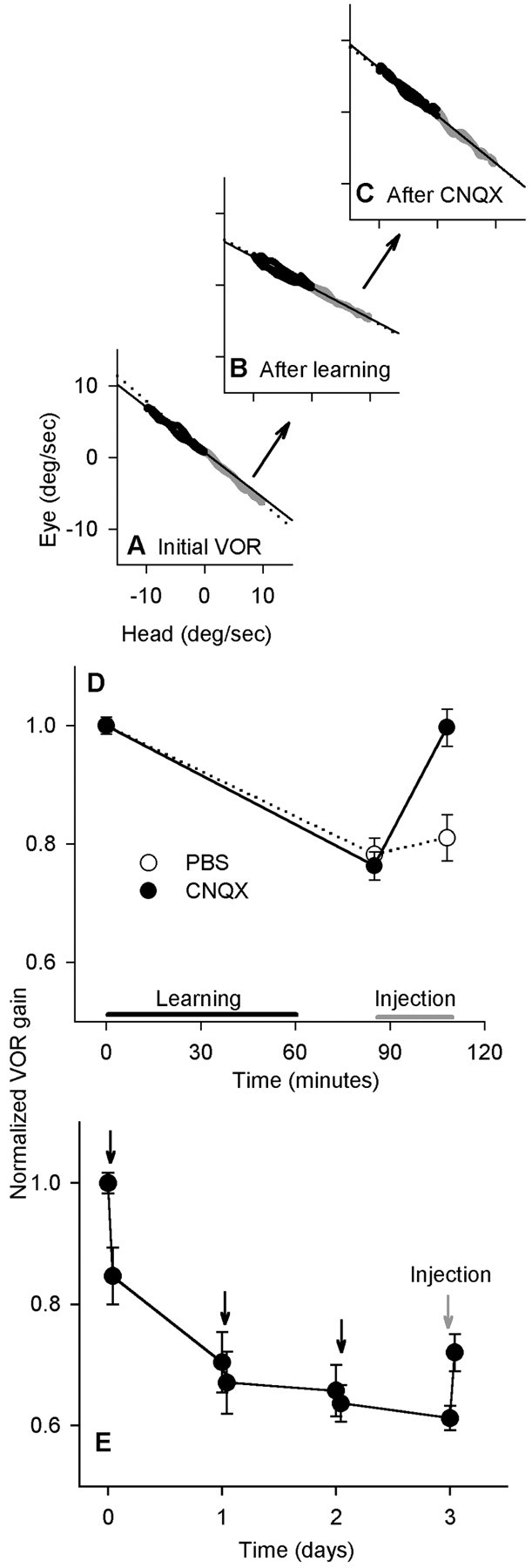
Injections of CNQX into the bilateral flocculi returned VOR gain to normal after the short-term but not the long-term protocol. VOR gain was measured at 2 Hz. A, Eye and head velocity before learning. Leftward (black) and rightward (gray) half-cycles were fit separately. B, After rotation and wearing 0.25× lenses for 60 min, the VOR gain decreased to 67% of baseline. C, After bilateral CNQX injections, the gain increased to 99% of the baseline value. D, Time course of the experiment. VOR gain values were normalized to a mean starting value of 1.0 for each cat; the actual initial gains ranged from 0.62 to 0.82. Sixty minutes of learning (black bar) were followed by injection (graybar) (n = 6 for each group; pooled data from cats H and K). E, In the long-term experiment, spectacles were worn continuously with forced rotation each day (black arrows). The VOR gain was measured at 2 Hz. On day 4, CNQX was injected bilaterally (gray arrow) (n = 6; pooled data from cats H and N).
