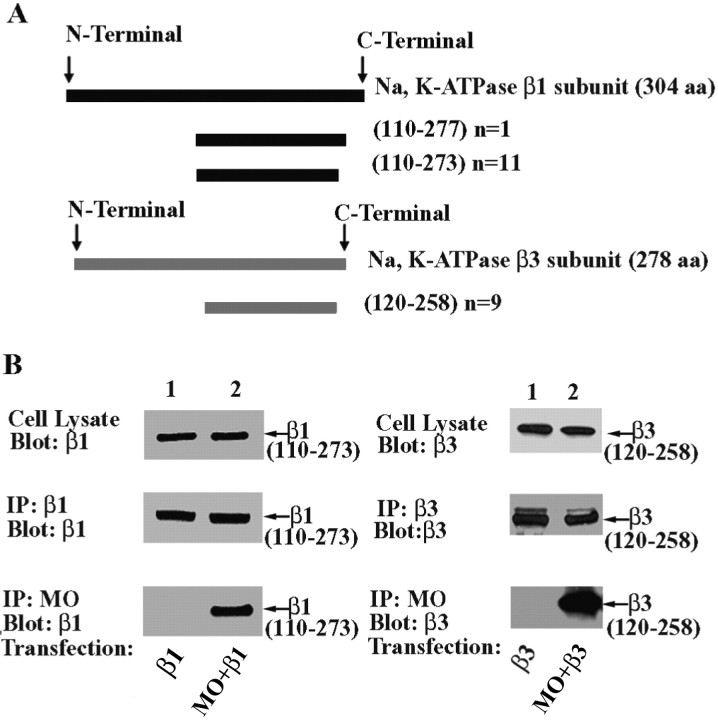
Figure 5.
MONaKA binds to C-terminal fragments of Na,K-ATPase β subunits. A, Results from the yeast two-hybrid screen. Both the short and full-length MONaKA sequences were used as baits in yeast two-hybrid screens. Of 21 positive clones, nine encoded amino acids 120–258 of the β3 subunit of the Na,K-ATPase. The other 12 clones encoded a portion of the C-terminal domain of the β1 subunit of the Na,K-ATPase. n indicates number of clones. B, Mouse MONaKA (MO) coimmunoprecipitates with the β1 and β3 subunit C-terminal fragments identified in the yeast two-hybrid screen (23 and 22 kDa, respectively). tsA201 cells were transfected with either the short or full-length versions of HA-tagged MONaKA, together with Myc-tagged Na,K-ATPase β1 or β3 subunit C-terminal fragments. Identical results were obtained for β1 (left panels) and β3 (right panels) subunit fragments. Western blot demonstrates that the β subunit fragment expression (top panels) and immunoprecipitation (IP)(middle panels) are similar in the absence or presence of MONaKA. A β subunit fragment band is observed in the MONaKA immunoprecipitate (bottom panels) only when β subunit fragment and MONaKA are transfected together. No bands were seen when vector only was used as control (data not shown).