Figure 2.
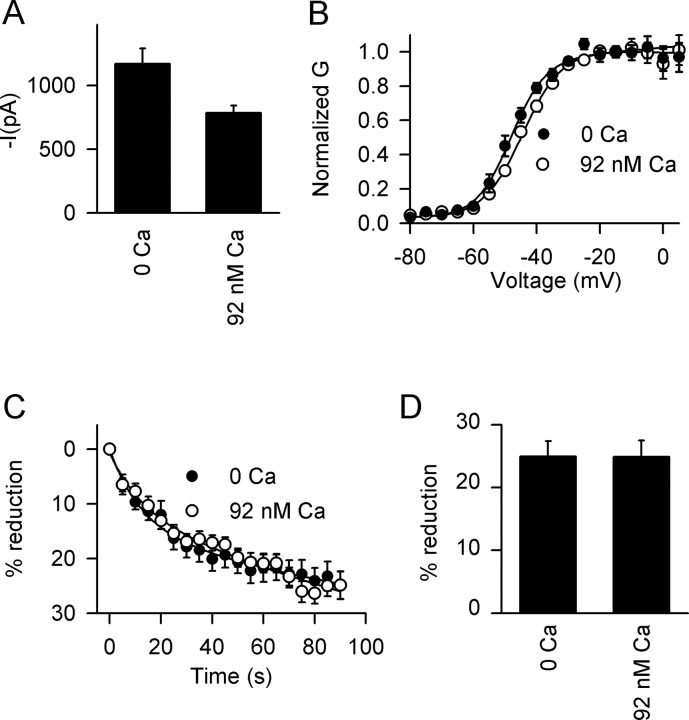
Effect of [Ca2+]i on Na+ current and its modulation by OAG in mouse hippocampal neurons. A, Amplitude of Na+ current with the indicated concentrations of free [Ca2+]i. Free Ca2+ was calculated using WebMaxchelator v2.10 with intracellular solutions containing 10 mm EGTA. Mean peak Na+ current was 785 ± 57 pA in 92 nm [Ca2+]i (n = 9) compared with 1169 ± 120 pA (n = 10) in 0 nm. B, Effect of [Ca2+]i on steady-state activation. Half-maximal activation (V1/2) for 0 nm [Ca2+]i was -45.1 ± 1.4 (n = 8) and for 92 nm [Ca2+]i was -44.8 ± 1.9 (n = 5; p > 0.05). C, Time course of modulation by OAG with 0 nm (filled circles) and 92 nm (open circles) [Ca2+]i. The data were normalized to the current measured before OAG application. D, Maximal effect of 50 μm OAG on peak Na+ current as a function of [Ca2+]i. Mean reductions were 24.9 ± 2.5% at 0 nm Ca2+ (n = 14) and 24.9 ± 2.6% at 92 nm Ca2+ (n = 8).