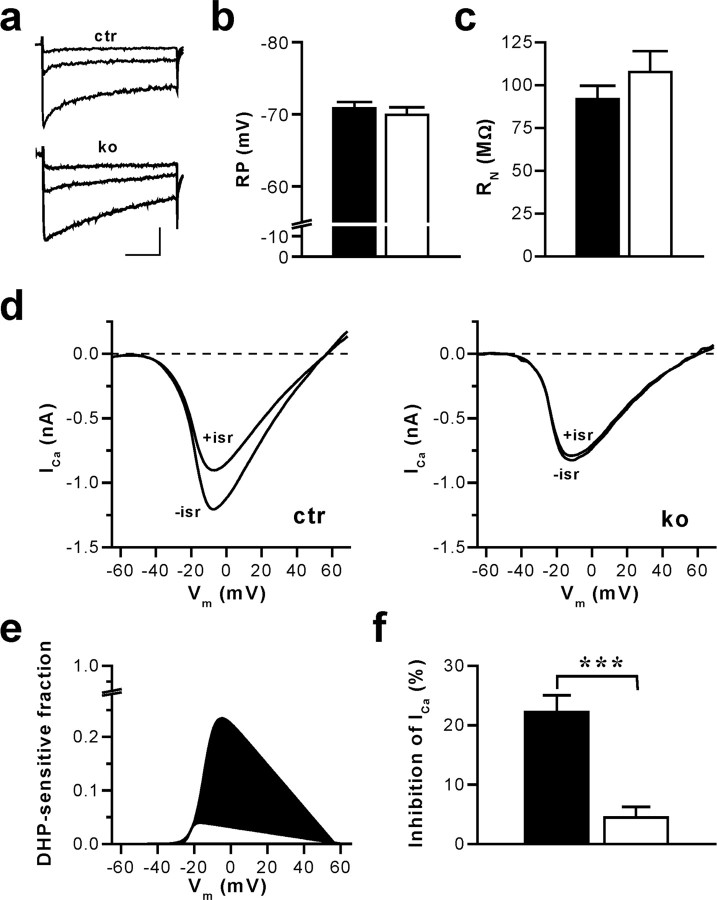
Figure 1.
CA1 pyramidal cells of mice with an inactivation of the CACNA1C gene (in Cav1.2HCKO) in the hippocampus display a nearly complete loss of L-type Ca2+ currents without changes in RP and RN. a, Ca2+ channel currents evoked by voltage-clamp steps in pyramidal neurons of hippocampal slices from control (ctr) and Cav1.2HCKO (ko) mice. The traces illustrated correspond to test potentials of -30, -20, and -10 mV. The holding potential was -65 mV, and 2 mm Ca2+ was used as a charge carrier. Calibration: 50 ms, 100 pA. b, Average RP measured in CA1 neurons of hippocampal slices from control (▪) (n = 13 cells from 6 mice) and Cav1.2HCKO (□) (n = 10 cells from 6 mice) mice in the current-clamp mode. Means + SEM are shown. c, Average RN of hippocampal CA1 neurons from control (▪) (n = 8 cells from 5 mice) and Cav1.2HCKO (□) (n = 6 cells, 5 mice) mice determined by injecting hyperpolarizing currents from a membrane potential of -70 mV. Means + SEM are shown. d, Representative examples of whole-cell Ca2+ currents (ICa) evoked by voltage-clamp ramps from -80 to +80 mV (0.5 ms/mV) in hippocampal CA1 neurons from ctr and ko mice before (-isr) and after (+isr) application of the L-type channel blocker isradipine (10 μm). The holding potential was -65 mV, and 2 mm Ca2+ was used as a charge carrier. e, Fraction of the total voltage-dependent Ca2+ inward current blocked by isradipine for the representative examples shown in d. Fitted I-V curves of the DHP-sensitive current component in control (filled in black) and Cav1.2HCKO (filled in white) mice, normalized to the corresponding peak inward current in the absence of isradipine (for details on fit function, see Materials and Methods), are represented. f, Average component of the total voltage-dependent Ca2+ current block by isradipine. The reduction of the peak inward current in hippocampal CA1 neurons from control (▪) (n = 14 cells from 6 mice) and Cav1.2HCKO (□) (n = 9 from 5 mice) mice, shown in percentage, is represented. Data are means ± SEM (***p < 0.001).