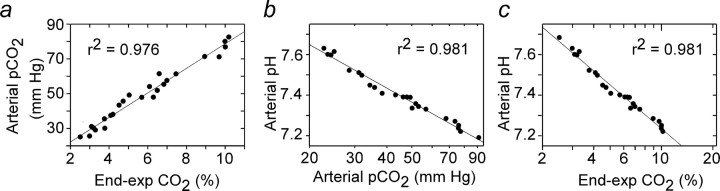
Figure 1.
Blood gases in rats exposed to hypercapnia at steady state. a, Relationship between arterial pCO2 (from blood gas analyzer) and end-expiratory CO2 (from capnometer). b, Relationship between pHa and arterial pCO2 (both from blood gas analyzer). c, Relationship between pHa and end-expiratory CO2 (from capnometer). Data are from six rats, three of which were treated with KYN. Note linear semilog relationship between pHa and end-expiratory CO2.