Figure 4.
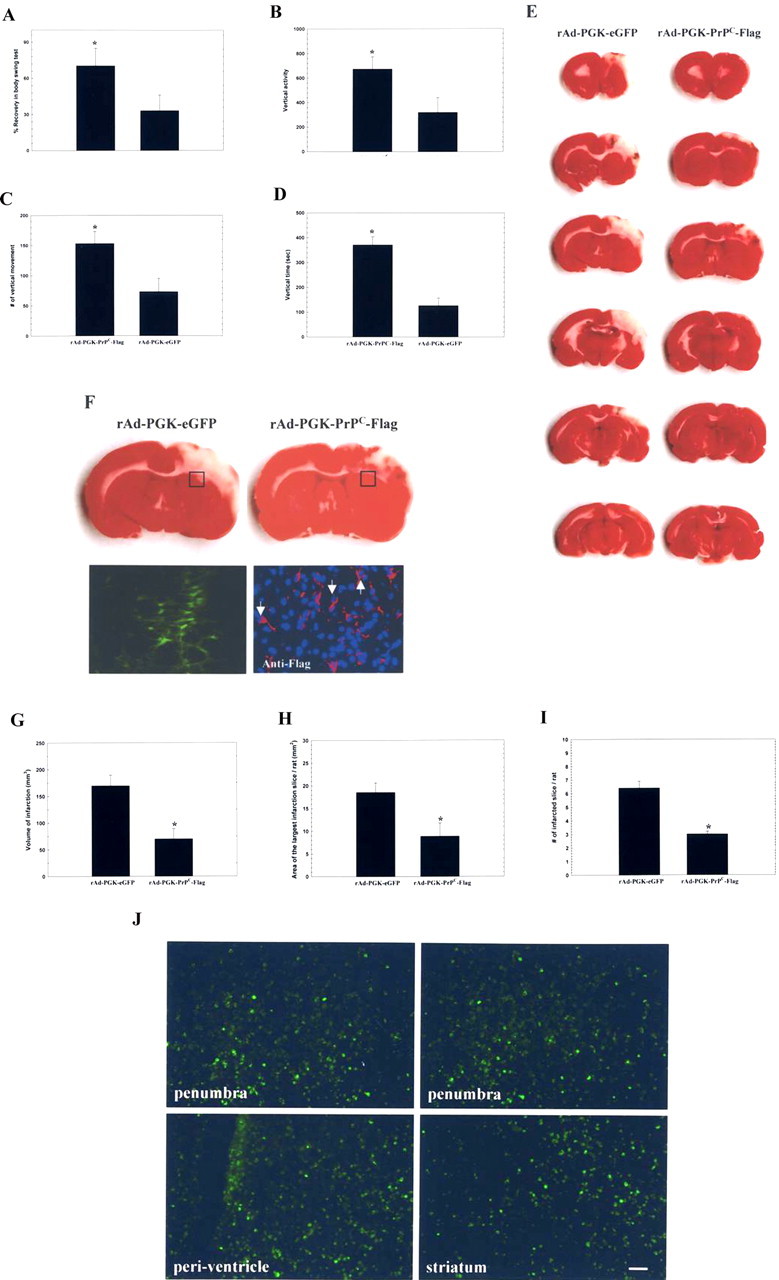
Intracerebral injection of rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag improves neurological dysfunction and reduces infarcted volume in stroke rats. A–D, Three days after cerebral ischemia, body asymmetry trials, and locomotor activities, three vertical parameters were examined in each experimental rat. These showed significant improvement in rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag-treated rats compared with rAd-PGK-eGFP-treated control rats. E, Injection of rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag significantly reduced cortical infarction compared with rAd-PGK-eGFP-treated rats. The white area represents the infarcted zone in the right cerebral cortex by TTC staining. F, Under immunofluorescence, rats receiving rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag showed expression of Flag [red-Cy3 and blue-4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI)] in the representative square area (□), compared with rats receiving rAd-PGK-eGFP, showing expression of eGFP (green-eGFP) in the square area. G, The volume of infarction was significantly reduced in rats treated with rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag compared with the control (rAd-PGK-eGFP) group. H, The area with the largest infarction in a section from a given rat was significantly diminished by rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag treatment. I, Finally, the number of infarcted sections per rat was also reduced by rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag treatment. J, The results of fluorescent microscopy of rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag-infected cells in ischemic brains were shown to be widely distributed in the peri-infarcted region, striatum, and periventricular area.
