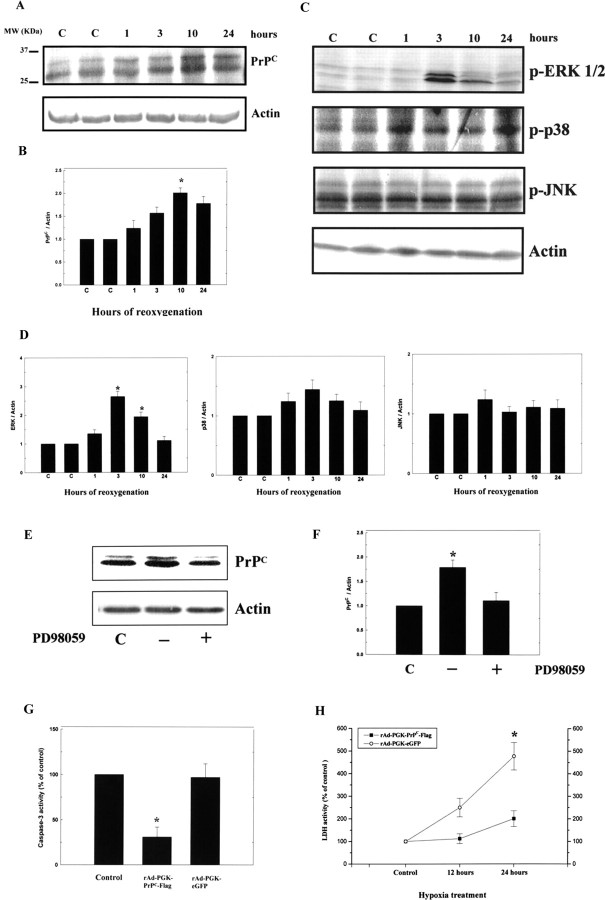
Figure 7.
Hypoxia–reoxygenation induces translation of PrPC and ERK1/2 in primary cortical cultures. A, primary cortical cultures were placed in a hypoxic chamber (95% N2 and 5% CO2, 37°C) for 12 h and returned to a normoxic incubator (95% air and 5% CO2, 37°C) for different lengths of time (1, 3, 10, and 24 h), after which, total protein was extracted for Western blot analysis of PrPC. B, Densitometric analysis of the Western blot, the ratio of PrPC/actin was taken as 1 for nonhypoxic cells, which represents the control (C). The mean ± SEM is shown. *p < 0.05 versus control. The time-dependent changes in PrPC expression are depicted. C, Primary cortical cultures were treated as above, and total protein was then extracted for Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK expression. D, Densitometric analysis of the Western blot, the ratio of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK/actin were taken as 1 for nonhypoxic cells, which represents the control. E, Primary cortical cultures were treated as above and total protein was then extracted for Western blot analysis of PrPC expression with or without addition of inhibitor of PD98059. F, Densitometric analysis of the Western blot, the ratio of PrPC/Actin were taken as 1 for nonhypoxic cells, which represents the control. G, The results show that N18 cells infected with rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag subjected to hypoxia for 12 h exhibited significantly reduced caspase-3 activity compared with that of rAd-PGK-eGFP. H, The rAd-PGK-PrPC-Flag-infected N18 cells showed much reduced LDH activity after 24 h of hypoxic treatment compared with that of rAd-PGK-eGFP. The mean ± SEM is shown. *p < 0.05 versus control. C, Control.