Figure 5.
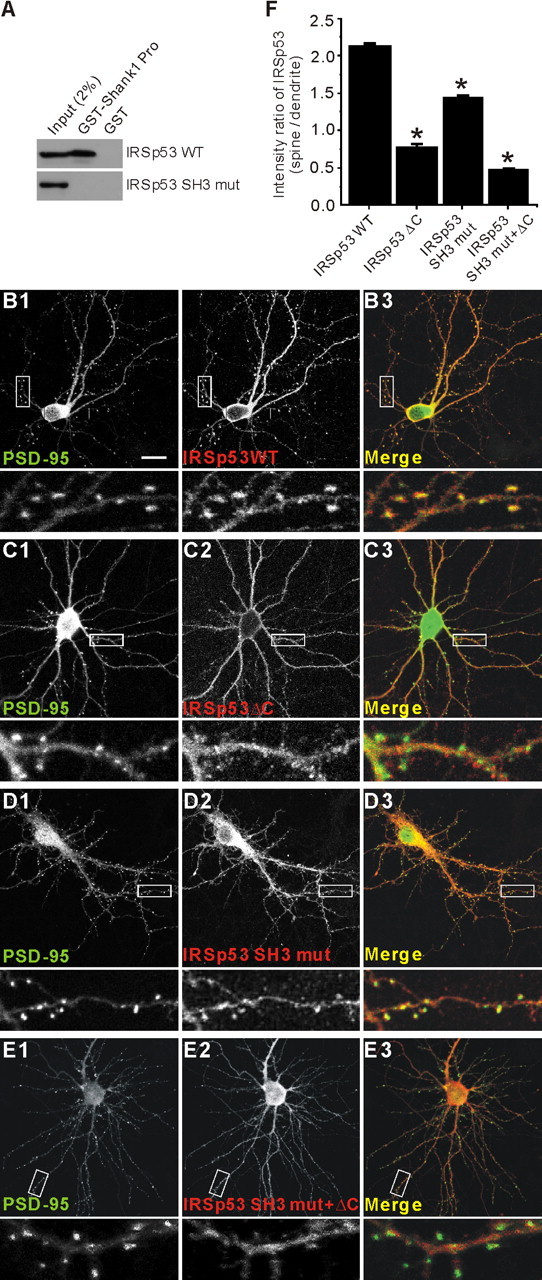
Both the C terminus and the SH3 domain are important for the synaptic localization of IRSp53. A, Loss of Shank binding in an IRSp53 mutant with a point mutation in the SH3 domain (IRSp53 SH3 mut; I403P). HEK293 cell lysates transfected with IRSp53 (WT or SH3 mut) were pulled down by GST-Shank1 Pro (IRSp53-binding proline-rich region in Shank1) and immunoblotted with IRSp53 antibodies. B-E, Cultured hippocampal neurons (17 DIV) were cotransfected with PSD-95-EGFP and HA-IRSp53 constructs; wild-type (IRSp53 WT; B), a PSD-95 binding-defective mutant that lacks the last four residues (IRSp53 ΔC; C), a Shank binding-defective mutant with a point mutation in the SH3 domain (IRSp53 SH3 mut; D), or a double mutant (IRSp53 SH3 mut plus ΔC; E). Transfected neurons were visualized by double immunofluorescence staining for EGFP (for PSD-95) and HA (for IRSp53) at 19 DIV. To measure synaptic localization, the immunofluorescence intensity of IRSp53 at a PSD-95-positive dendritic spine was compared with that in an adjacent dendritic trunk. Scale bar, 20 μm. F, quantitative analysis of the synaptic localization of IRSp53.
