Figure 5.
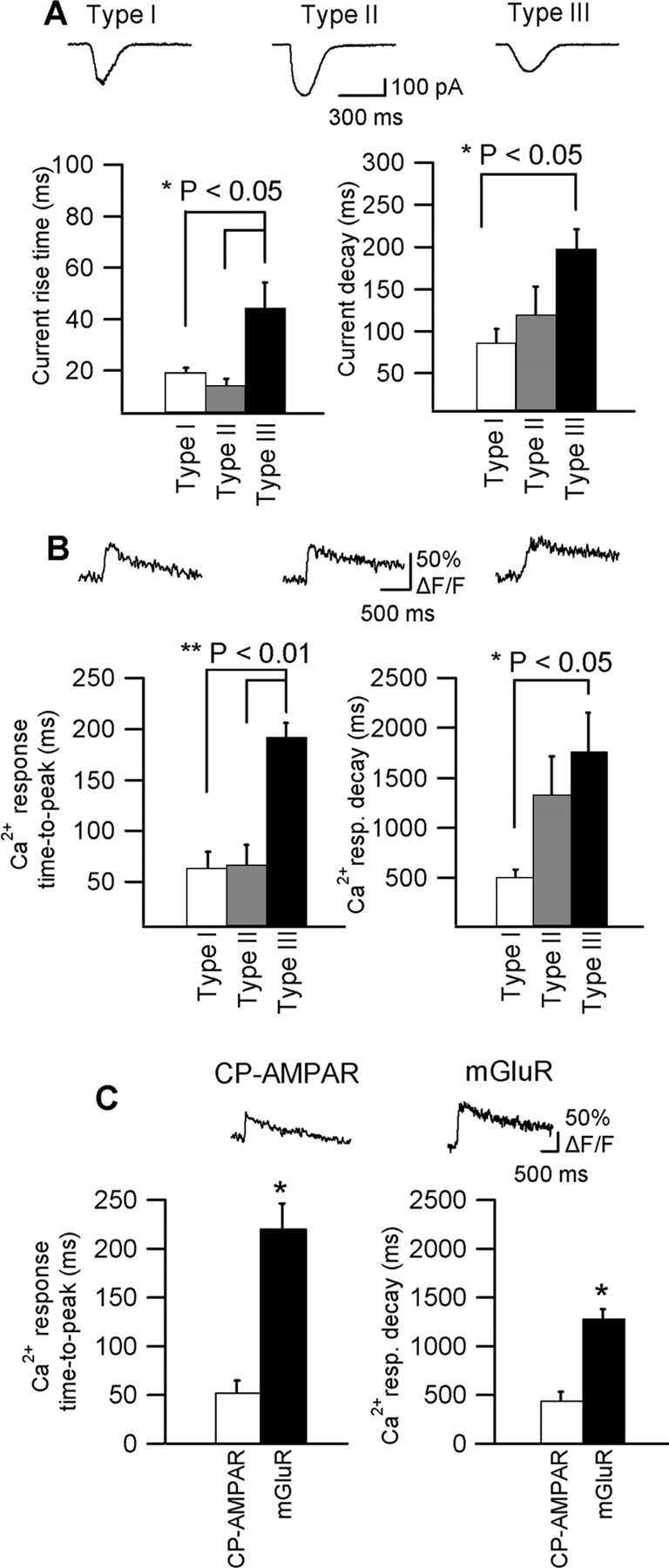
Response-specific time course. A, Representative examples of three types of glutamate-evoked currents (Vh =-60 mV): type I (inwardly rectifying), type II (intermediate), and type III (outwardly rectifying), and bar graphs of the mean rise (left) and decay times (right) of currents for the three response types for all cells. B, Ca2+ transients associated with the three types of membrane currents shown in A and bar graphs of the mean time-to-peak (left) and decay time (right) of Ca2+ transients for all cells. Membrane currents and Ca2+ transients of type I and II responses displayed significantly faster rise time than those of type III response. Type III response showed significantly slower decay than type I response (**p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; ANOVA). C, Representative examples of CP-AMPAR-mediated (in AP-5 + E4CPG) and mGluR-mediated (in AP-5 + CNQX) Ca2+ transients measured with the low-affinity Ca2+ indicator Fluo-5F; bar graphs indicate the mean time-to-peak (left) and decay time (right) of Ca2+ transients for all cells (CP-AMPAR, n = 5; mGluR, n = 5).
