Figure 2.
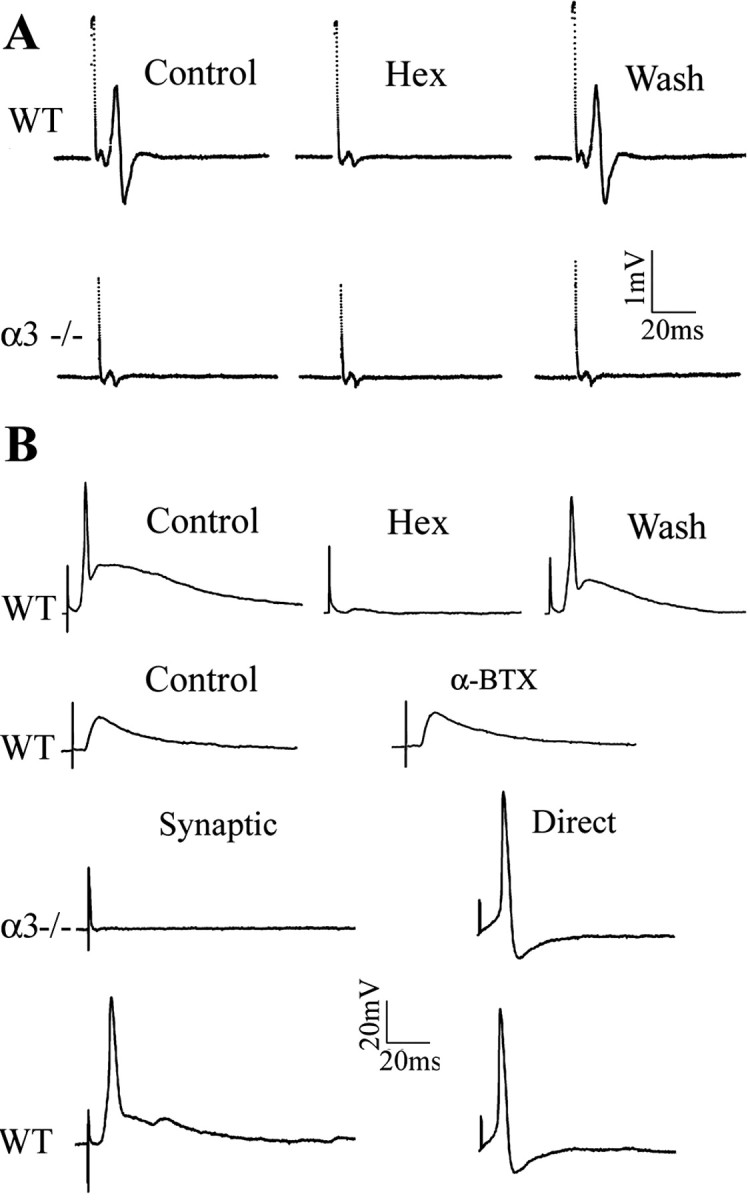
No postganglionic compound action potential or fast EPSPs on sympathetic neurons in α3–/– superior cervical ganglion. A shows postganglionic compound action potentials and preganglionic potentials recorded from the sympathetic trunk of a P7WT SCG (top traces) in response to suprathreshold stimuli to the preganglionic nerve. In WT ganglia, hexamethonium (Hex) (100 μm) reversibly blocked the compound action potential but had no effect on the preganglionic potential. In P7 α3–/– ganglia (bottom trace), suprathreshold stimuli to the preganglionic nerve failed to evoke postganglionic compound action potentials, whereas the preganglionic potentials were unchanged. B, Stimulating the preganglionic nerve evoked large suprathreshold EPSPs from a P8 WT sympathetic neuron recorded intracellularly; the EPSPs were reversibly blocked by hexamethonium (100μm) but unaffected byαBgt (0.5μm). Stimulating the preganglionic nerve failed to produce any change in membrane potential on a P8 α3–/– sympathetic neuron, demonstrating that fast synaptic EPSPs are absent inα3–/– ganglia. Direct intracellular current injection, conversely, evoked fast, overshooting action potentials (right) on both WT and α3–/– neurons, indicating that α3–/– neurons do not require fast synaptic transmission to express voltage-gated currents that underlie the action potential.
