Figure 4.
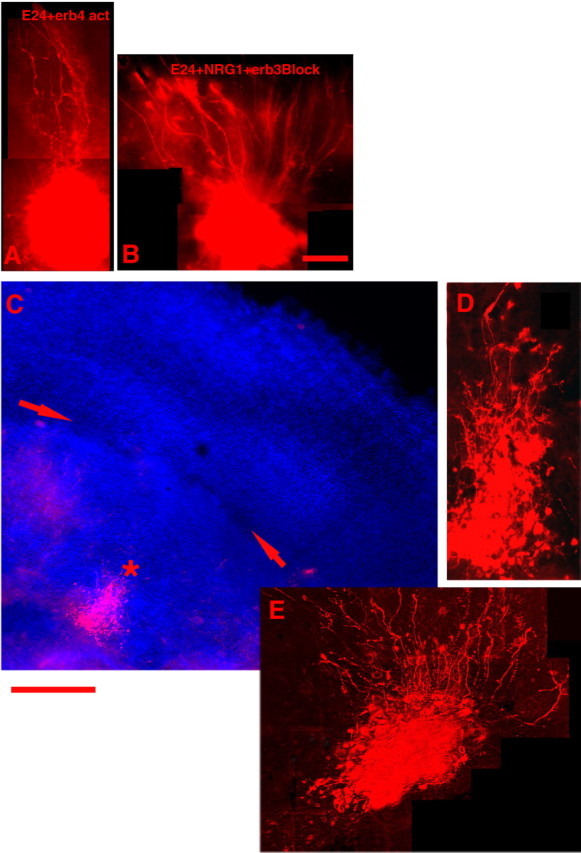
ErbB receptor activation or blockade. A illustrates the effect of adding an activating antibody to the media during organotypic culture of a slice of E24 MAM-treated ferret cortex. The erbB4 activation results in improved morphology of radial glia. B, An example of an E24 MAM-treated culture that received supplemental NRG1 in the medium. The addition of an erbB3 blocking antibody prevents improved morphology usually afforded by the addition of NRG1. C, A coculture with the E24 MAM-treated slice and a normal cortical implant; the red arrows indicate the boundary between the two. Soluble erbB4 receptors were added to the culture media. The normal implant would normally release a factor that improves radial morphology of the radial glia. The soluble erbB4 binds to available NRG1 and prevents radialization by the endogenous factor, suggesting that the diffusible factor in normal cortex is NRG1. D, A higher-power view of the injection shown in C (asterisk). E, An example of a dextran injection taken from a different coculture treated in the same way. Scalebars: (in B) A, B, 200μm; (below C) C, 400 μm; (below C) D, E, 200 μm.
