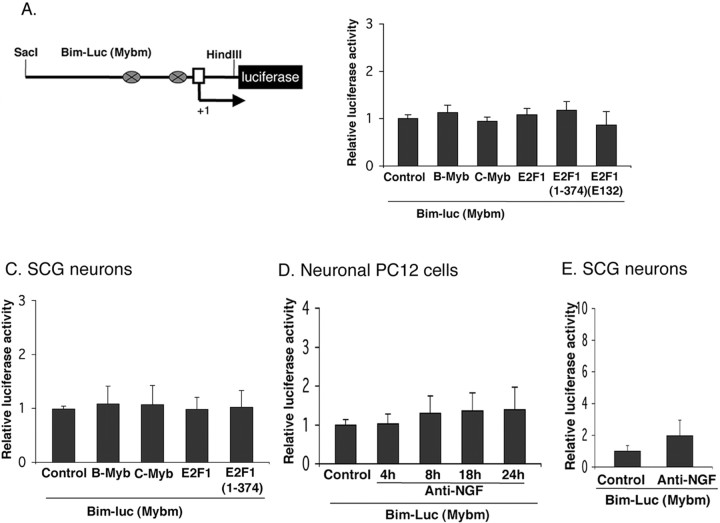
Figure 6.
The activation of Bim promoter by NGF withdrawal or B-myb, C-myb, E2F1, and an E2F truncation mutant lacking a transactivation domain in neuronal PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons requires myb binding sites. A, Schematic representation of rat mutant Bim promoter-driven luciferase reporter constructs. The mutant lacks two myb binding sites shown as ovals. B, C, The activation of Bim promoter by B-myb, C-myb, E2F1, and E2F1(1–374) requires myb binding sites. Neuronal PC12 cells (B) and sympathetic neurons (C) were cotransfected with 0.5 μg of mutant Bim–luc reporter and 0.1 μg of the Renilla luciferase expression construct pRL–CMV with 0.5 μg of empty pCMV vector (Control), B-myb, C-myb, E2F1, E2F1(1–374), or E2F1(E132) and maintained for 24 h, after which luciferase assays were performed. Data were normalized as in Figure 2 and represent means ± SEM for three or four experiments. D, Induction of Bim promoter-driven luciferase activity after NGF withdrawal in neuronal PC12 cells requires myb binding sites. Neuronal PC12 cells were transfected with 0.5 μg of mutant Bim–luc reporter and 0.1 μg of the Renilla luciferase expression construct pRL–CMV and were maintained with or without NGF for the indicated times, after which luciferase assays were performed. The data are reported as relative firefly luciferase activity normalized to Renilla luciferase activity and represent means ± SEM of four experiments. E, Induction of Bim promoter-driven luciferase activity after NGF withdrawal from sympathetic neurons requires myb binding sites. Sympathetic neurons were transfected and assayed for luciferase activity as described in D, except that they were maintained with or without NGF for 18 h. The data are means ± SEM of three experiments.