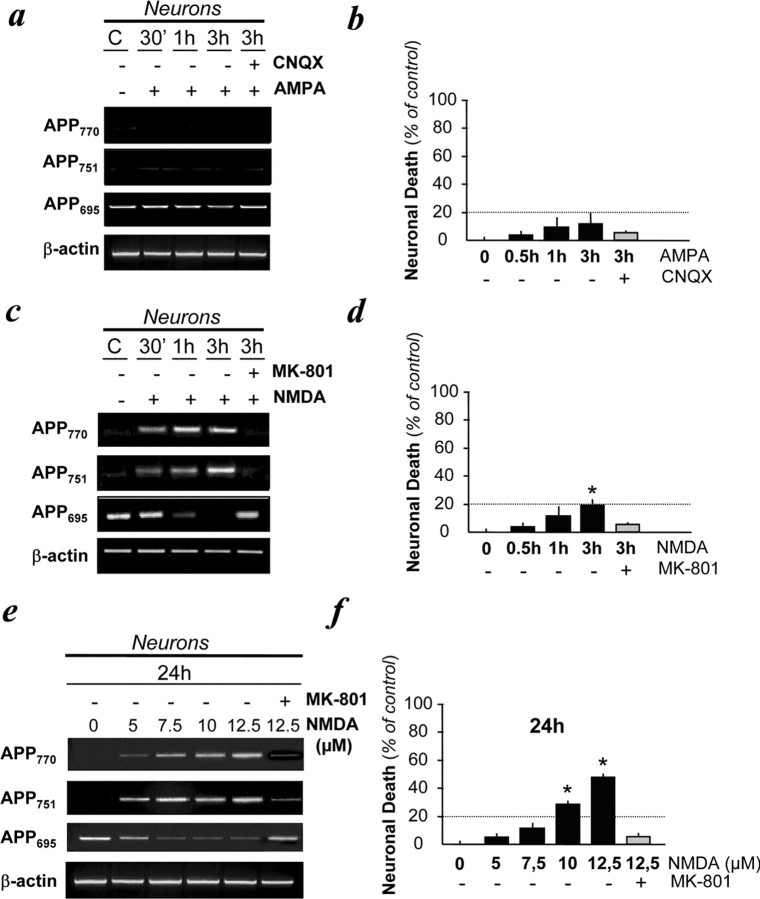
Figure 1.
Expression of KPI-APP mRNAs in cultured cortical neurons subjected to NMDA-induced excitotoxicity. a, Transcriptional expression of APP isoforms in neurons exposed to AMPA (50 μm) in the presence of the AMPA antagonist CNQX (10 μm) for 30 min, 1 h, and 3 h. All conditions were performed with MK-801 (10 μm). b, Estimation of neuronal cell death in paradigms presented in a by determining the activity of LDH released by dying neurons. Statistical analysis was realized by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Dunn's test (n = 16; p < 0.001). c, Transcriptional expression of APP isoforms in neurons exposed to NMDA (50 μm) in the presence or absence of MK-801 (10 μm) for 30 min, 1 h, and 3 h. All conditions were performed with CNQX (10 μm). d, Estimation of neuronal cell death in paradigms presented in c. Statistical analysis was realized by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Dunn's test (n = 16; p < 0.001). e, Dose-dependent increased expression of KPI-APPs mRNAs in neurons exposed to NMDA in the presence or absence of MK-801 (10 μm) for 24 h. All conditions were performed with CNQX (10 μm). f, Estimation of neuronal cell death in paradigms presented in e. Note that the 24 h application of 7.5 μm NMDA can lead to neuronal death similar to that observed by treating neurons with 50 μm NMDA for 3 h. Statistical analysis was realized by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni-Dunn's test (n = 16; p < 0.001). C, Control.