Figure 7.
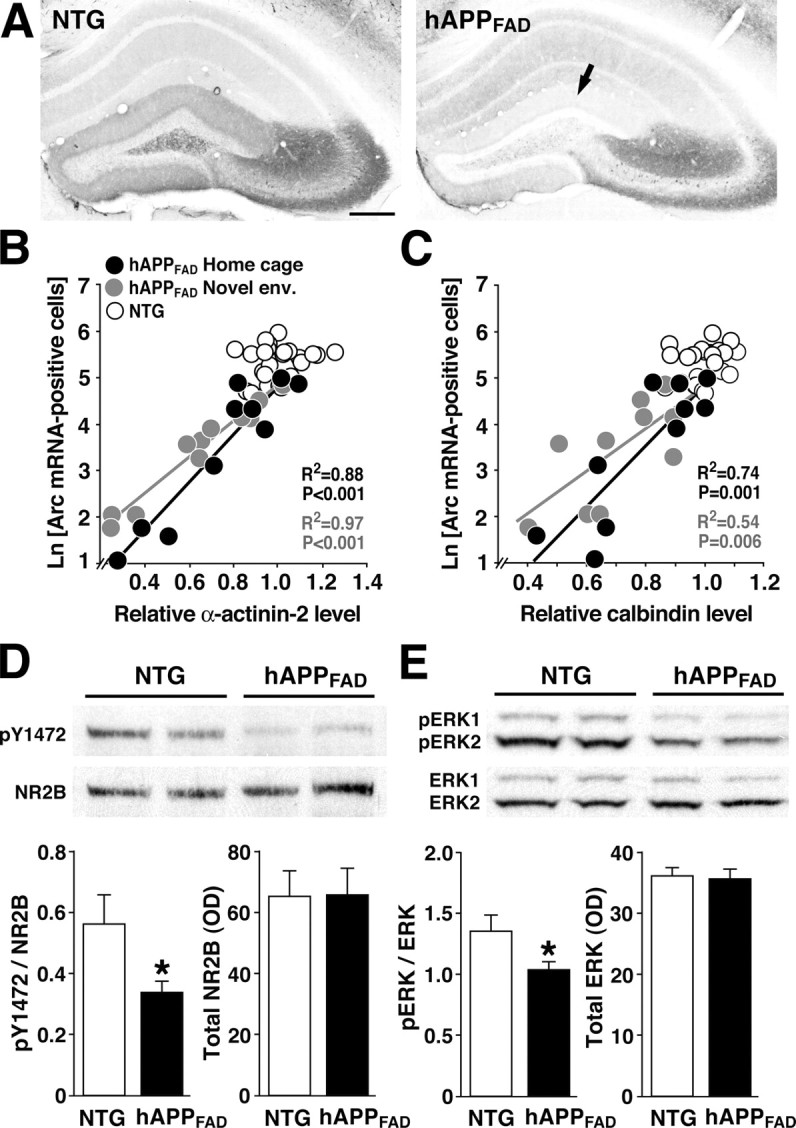
Deficits in Arc expression are associated with reductions in key components of the NMDA receptor-dependent signaling pathway. A-C, Arc expression deficits in granule cells of hAPPFAD mice are tightly linked to the depletion of α-actinin-2 in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus. Coronal brain sections of NTG and hAPPFAD mice that had (gray dots) or had not (black dots) explored a novel environment were analyzed by in situ hybridization for Arc or immunostained for α-actinin-2 or calbindin. Representative sections in A illustrate robust expression of α-actinin-2 in the molecular layer of an NTG control (left) and depletion of α-actinin-2 in the molecular layer of an hAPPFAD mouse (right, arrow). Scale bar, 250 μm. At baseline and after environmental exploration, granule cell expression of Arc correlated strongly with levels ofα-actinin-2 (B), calbindin (C), and Fos (data not shown) in hAPPFAD mice but not in NTG controls. R2 and p values in B and C refer to hAPPFAD mice only. Novel env., Novel environment; Ln, natural log. D, E, Levels of phosphorylated (activated) NR2B and ERK1/2 are reduced in the dentate gyrus of hAPPFAD mice. Western blot analysis of phosphorylated tyrosine residue 1472 of NR2B (pY1472) and total NR2B (D) levels and of dually phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) and total ERK1/2 (E) levels illustrates reduced levels of putatively activated NR2B and ERK1/2 in the dentate gyrus of hAPPFAD mice compared with NTG controls. Quantitation of bands on comparable blots (bottom) revealed significant reductions in the ratios of phospho/total NR2B (D) and in phospho/total ERK1/2 (E) in hAPPFAD mice compared with NTG controls and no change in the levels of total NR2B and total ERK1/2. n = 9-10 mice per genotype. *p < 0.05 (Student's t test). Error bars indicate SEM.
