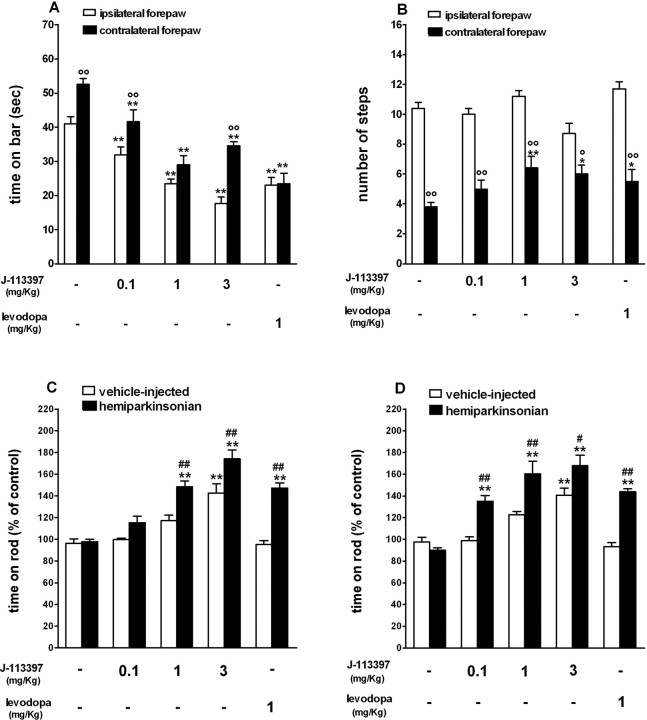
Figure 3.
J-113397 and levodopa relieved akinesia/hypokinesia and attenuated motor asymmetry in hemiparkinsonian rats. A-D, Systemic (intraperitoneal) injection of J-113397 (0.1-3 mg/kg) or levodopa (1 mg/kg plus 15 mg/kg benserazide) reduced the time spent on the blocks (in seconds) and attenuated motor asymmetry in the bar test (A), increased the number of steps of the contralateral forepaw in the drag test (B), and improved overall motor performance (calculated as percentage of the control session) in the rotarod test (C, D). Motor asymmetry was evaluated by separate measures at the paws ipsilateral and contralateral (parkinsonian) to the lesioned side. The bar and drag tests (A, B) were performed 20 min after injection; the rotarod test was performed 20 min (C) and 70 min (D) after injection. A-D, Data are mean ± SEM of six to eight determinations obtained from 45 hemiparkinsonian and 35 vehicle-injected rats. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 versus saline-treated rats. °p < 0.05; °°p < 0.01 versus the ipsilateral paw. #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01 versus vehicle-injected rats (ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post hoc test). Error bars represent SEM.