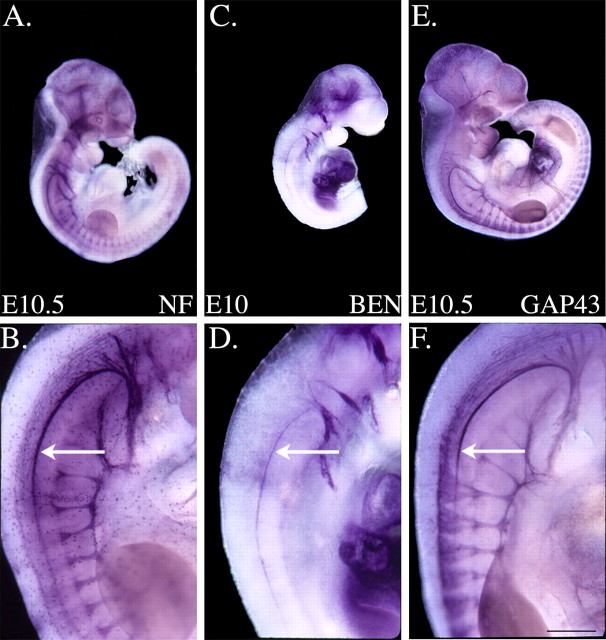
Figure 2.
Anti-BEN labels the entire rostrocaudal extent of the SAN. A-F, Whole mouse embryos were labeled with anti-NF, anti-BEN, or anti-GAP43. The higher-magnification images in B, D, and F represent cervical spinal cord levels of the labeled embryos shown in A, C, and E, respectively. Anti-NF (A, B) brightly labels the hook-shaped SAN (arrow), as well as a variety of axons and cranial nerves/ganglia in an E10.5 mouse embryo. In a whole E10 mouse embryo, anti-BEN (C, D) rather selectively labels the SAN (arrow) and a small subset of cranial nerves/ganglia. Anti-GAP43 (E, F) labels the SAN (arrow) and a significant number of axons/nerves in a whole E10.5 mouse embryo. The thicker appearance of the hook-shaped axon bundle in the anti-NF and anti-GAP43 panels is likely attributable to these more general axonal markers, but not anti-BEN, also labeling the vagus nerve, which runs alongside the SAN. Scale bar, 0.5 mm.