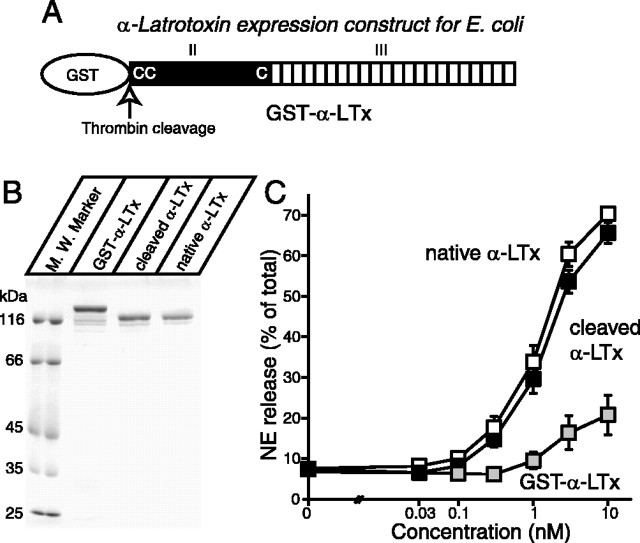
Figure 1.
Analysis of recombinant α-latrotoxins. A, Schematic representation of mature α-latrotoxin and recombinant α-latrotoxins. Mature α-latrotoxin is composed of two domains (domains II and III). The conserved N-terminal domain is shown (II). Locations of the only three cysteine residues that are conserved in all latrotoxins are shown as C's. The C-terminal region, composed of 22 ankyrin-like repeats, is shown (III). B, Analysis of purified recombinant α-latrotoxins. The recombinant α-latrotoxins (GST-α-LTx, GST-cleaved α-LTx; ∼1-2 μg) along with native α-latrotoxin were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. C, GST-cleaved recombinant α-latrotoxin stimulates Ca2+-dependent exocytosis with a similar potency to native α-latrotoxin. A stimulation of NE secretion from PC12 cells by indicated concentrations of native α-LTx (white squares; n = 12), cleaved recombinant α-LTx (black squares; n = 10), and GST-α-LTx (gray squares; n = 3) is shown. Error bars indicate SEM.