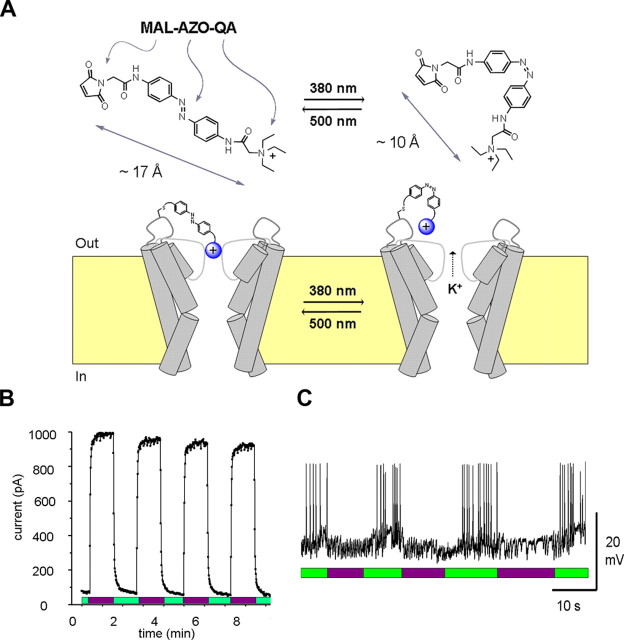
Figure 8.
Design and use of light-activated SPARK channels. A, The channels contain a synthetic photoswitch molecule (MAL-AZO-QA; top) that changes length from 17Å (trans) to 10Å (cis) during exposure to light. Covalent attachment of the molecule to the outside of a Shaker K+ channel (bottom) allows the pore-blocking QA group (blue ball) to be retracted or advanced into the pore with different wavelengths of light. B, Rapid control of SPARK channels with light. Activation of the channels with 380 nm light (violet bars) and deactivation with 500 nm light (green bars). Data are from a membrane patch excised from a Xenopus oocyte expressing the H-SPARK channel. C, Expression of the H-SPARK channel in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons allows 380 nm light (violet bars) to suppress spontaneous action potential firing and 500 nm light (green bars) to restore activity. Modified from Banghart et al. (2004).