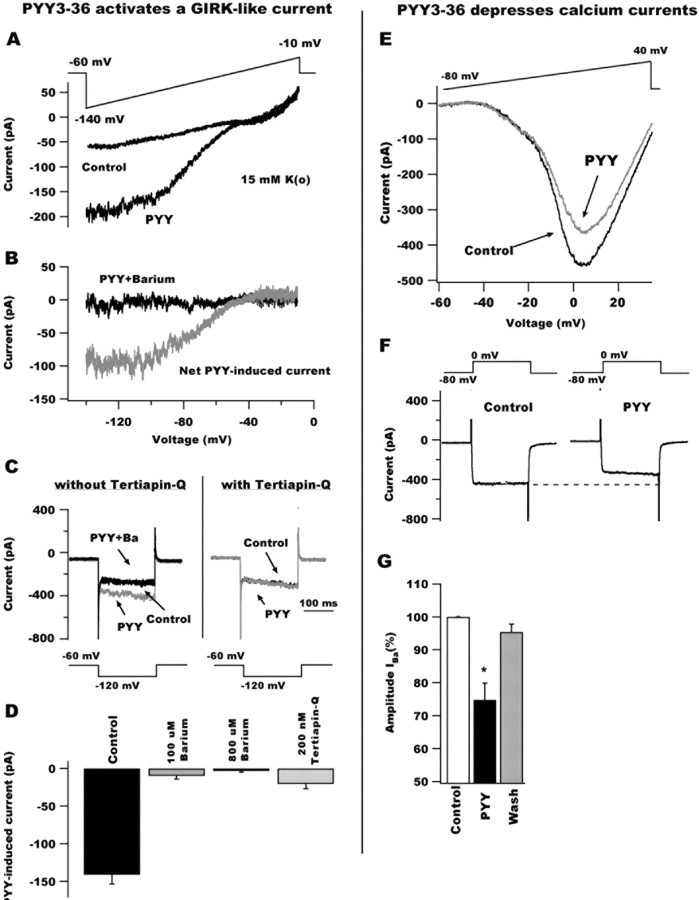
Figure 3.
PYY3-36 activates GIRK-like currents and depresses whole-cell calcium currents in POMC neurons. A, Voltage-ramp protocols (from -140 to -10 mV for 800 ms; top) revealed that PYY3-36 activates an inwardly rectifying current reversing at approximately -60 mV in 15 mm external potassium. B, The PYY3-36-induced current (gray trace) was attenuated by 800 μm barium (black) in the ACSF, consistent with an inwardly rectifying subtype. C, Voltage steps (see protocol at bottom) showing the effect of PYY3-36 on the inward current response in a typical arcuate GFP-expressing neuron in the absence (left) and the presence (right) of 200 nm Tertiapin-Q. Without pretreatment with Tertiapin-Q, PYY3-36 activated an inward current that, in addition, was blocked by 100 μm barium in the external solution. In the presence of Tertiapin-Q, PYY3-36 failed to activate the inward current. These data suggest that PYY3-36 activates a GIRK-like current in GFP-containing cells. D, Bar graph summarizing the effect of high (800 μm) and low (100 μm) doses of external barium and Tertiapin-Q (200 nm) on the current induced by PYY3-36 after voltage steps from -60 to -120 mV during 200 ms. E, PYY3-36 also reduced POMC current responses to voltage ramps from -60 to +40 mV. F, Whole-cell calcium current evoked by voltage steps from -80 to 0 mV (top) before (left) and during (right) PYY3-36 application to POMC cells. PYY3-36 depressed voltage-dependent calcium currents in these hypothalamic neurons. G, Bar graph showing the mean depressing effect of PYY3-36 on calcium current.