Figure 6.
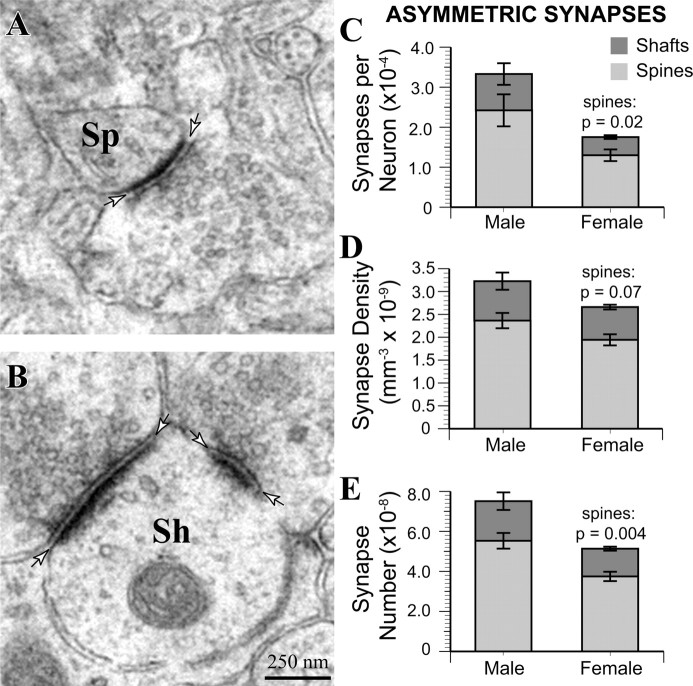
Male MeApd neurons are contacted by more asymmetric spine synapses. A, Example of an MeApd asymmetric spine synapse. B, Example of MeApd asymmetric shaft synapses. C, Asymmetric synapse-to-neuron ratio is greater in males (p = 0.04); male neurons have significantly more dendritic spine synapses (p = 0.02). D, The overall density of asymmetric synapses was statistically equivalent between males and females (p = 0.1), but males showed a trend toward greater density of asymmetric spine synapses than females (p = 0.07). E, The total number of asymmetric synapses was significantly greater in males than in females (p = 0.02). Furthermore, the total number of asymmetric spine synapses was also significantly greater (p = 0.004) in males, whereas the number of asymmetric shaft synapses was statistically equivalent (p = 0.1). Sh, Shaft synapse; Sp, spine synapse. Arrows indicate boundary of synaptic clefts.