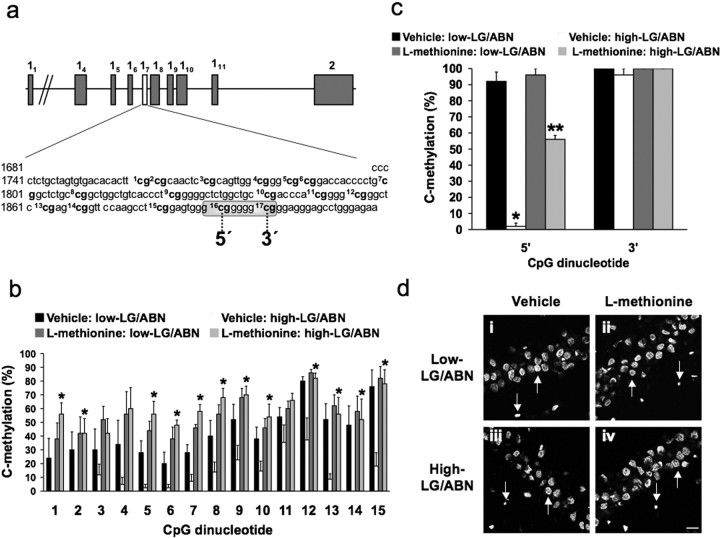
Figure 1.
Methionine alters cytosine methylation of GR promoter. a, Sequence map of the exon 17 GR promoter including the 17 CpG dinucleotides (bold) and the NGFI-A consensus sequence (McCormick et al., 2000) (encircled). b, c, Methylation analysis of the 17 CpG dinucleotides of the exon 17 GR promoter region from vehicle- and methionine-treated (100 μg/ml) adult high and low LG-ABN offspring (6-10 clones sequenced per animal; n = 4 animals per group; *p < 0.01). b, Percentage of methylated cytosine residues (mean ± SEM) for the first 15 CpG dinucleotides (*p < 0.05). c, Percentage of methylated cytosine residues (mean ± SEM) for the 5′ (site 16) and 3′ (site 17) CpG dinucleotides within the NGFI-A consensus sequence (*p < 0.0001; **p < 0.001). di-div, Confocal photomicrographs of representative 5-mC-positive neurons located within the CA1 hippocampal region of Ammon's horn from vehicle- and methionine-treated (100 μg/ml) adult high and low LG-ABN offspring (n = 6 animals per group with 9 sections per animal). Only large round nuclei corresponding to neuronal nuclei (indicated by arrows pointing upward) were included for analysis, and partial or smaller nuclei (indicated by arrows pointing downward) were not included in the quantification. Scale bar, 50 μm.