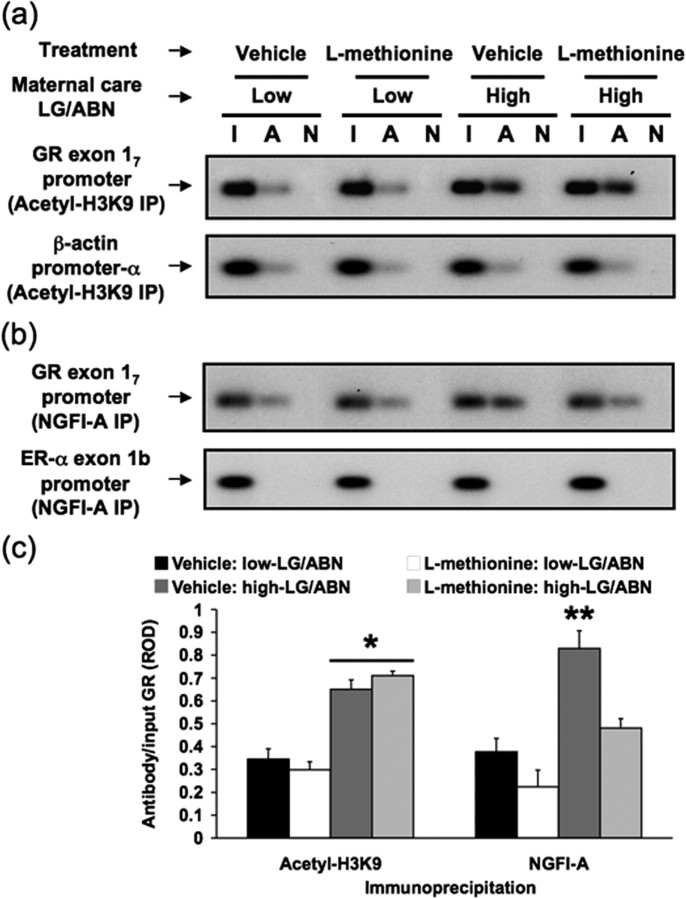
Figure 2.
Methionine eliminates maternal effect on NGFI-A binding independently of histone acetylation. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of the association between histone H3-K9 acetylation and NGFI-A binding to the exon 17 GR promoter sequence in hippocampal tissue from vehicle- and methionine-treated (100 μg/ml) adult offspring of high and low LG-ABNmothers(n = 4 animals per group). a, b, Lanes were loaded with non-immunoprecipitated input (I), acetylated histone H3-K9 (top) or NGFI-A (middle) primary antibody immunoprecipitated (A), or non-immune IgG antibody immunoprecipitated (N) hippocampal extracts. a, Representative Southern blot of the amplified exon 17 region from acetyl-histone H3-K9 immunoprecipitated hippocampal tissue (194 bp band). DNA loading was controlled using primers specific for the ubiquitously expressed β-actin promoter-α region (171 bp band). b, Representative Southern blot of the amplified exon 17 region of the GR from NGFI-A immunoprecipitated hippocampal tissue (194 bp band). Exon 1b ER-α promoter region, which does not contain NGFI-A recognition elements (493 bp), amplified from the same NGFI-A immunoprecipitated hippocampal tissue was run as a control for specificity and showed no signal. c, ROD (mean ± SEM) of exon 17 sequence amplified from acetyl-histone H3-K9 or NGFI-A immunoprecipitated hippocampal tissue from vehicle- and methionine-treated (100 μg/ml) adult high and low LG-ABN offspring (n = 4 animals per group; *p < 0.01; **p < 0.001).