Figure 1.
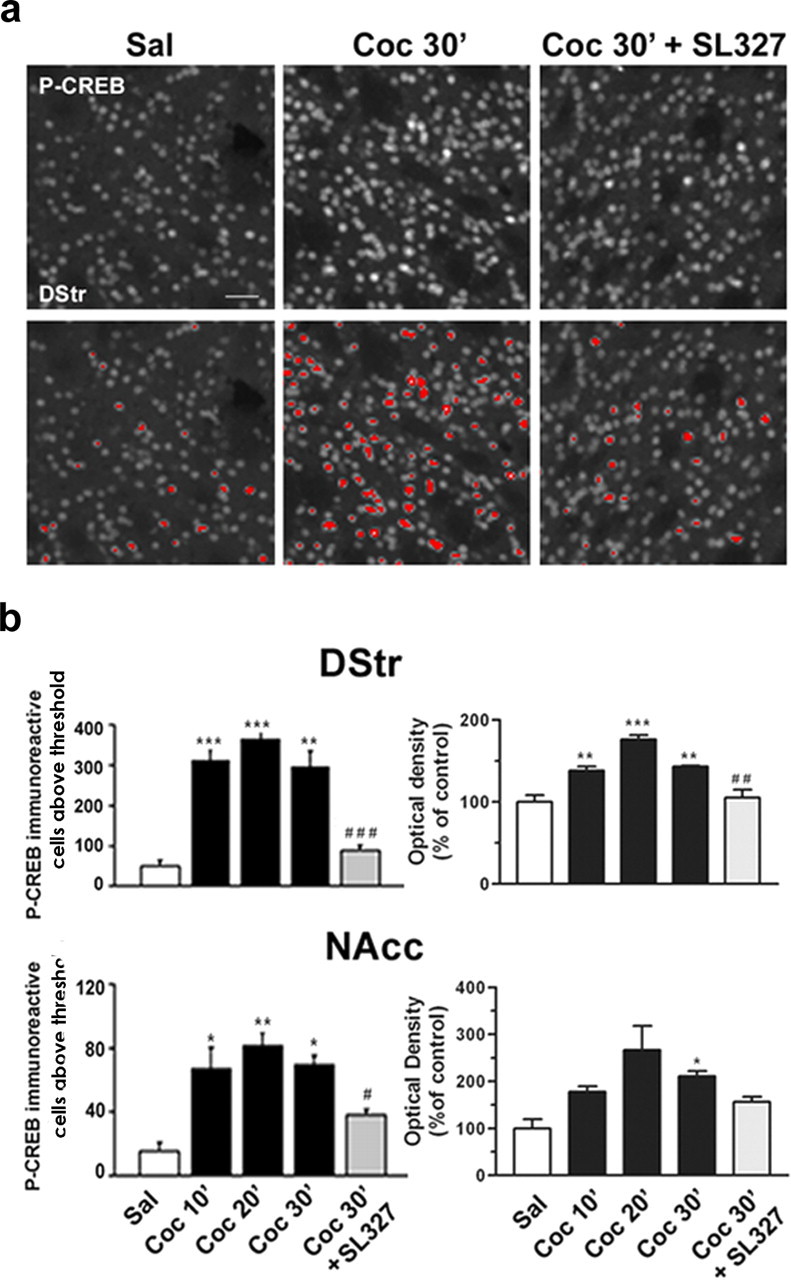
Cocaine-induced CREB phosphorylation is ERK dependent in the striatum. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with saline or cocaine (10 mg/kg) in the absence or presence of SL327 (50 mg/kg) before the cocaine. a, Top panels present immunocytochemical detection of phospho-Ser133-CREB in striatal neurons from mice injected with saline, cocaine, and SL327 before the cocaine. The bottom panels are a computerized representation of P-CREB-positive cells after the application of a threshold determined from saline-treated striatal sections. Cells with fluorescence above this threshold were counted. Scale bar, 40 μm. b, P-CREB immunoreactivity above a threshold (left panels) or global P-CREB immunofluorescence from the striatal sections (right panels) were analyzed in the dorsal striatum (DStr) and in the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) at 10, 20, or 30 min after cocaine injection (Coc 10′, Coc 20′, Coc 30′) in the absence or in the presence of SL327 (50 mg/kg; Coc 30′ plus SL327). Statistical comparisons in the left panels (means ± SEM; 4 mice per group) include one-way ANOVA (in DStr, F(4, 14) = 30.04 and p < 0.001; in NAcc, F(4, 14) = 11.90 and p < 0.001), followed by post hoc comparison (Scheffé's test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 Sal vs Coc; #p < 0.05 and ###p < 0.001 Coc 30′ vs Coc 30′ plus SL327). Statistical comparisons in the right panels (means ± SEM; 3-4 mice per group) include one-way ANOVA (in DStr, F(4, 14) = 22.36 and p < 0.001; in NAcc, F(4, 14) = 5.82 and p < 0.05), followed by post hoc comparison (Scheffé's test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 Sal vs Coc; and ##p < 0.001 Coc 30′ vs Coc 30′ plus SL327).
