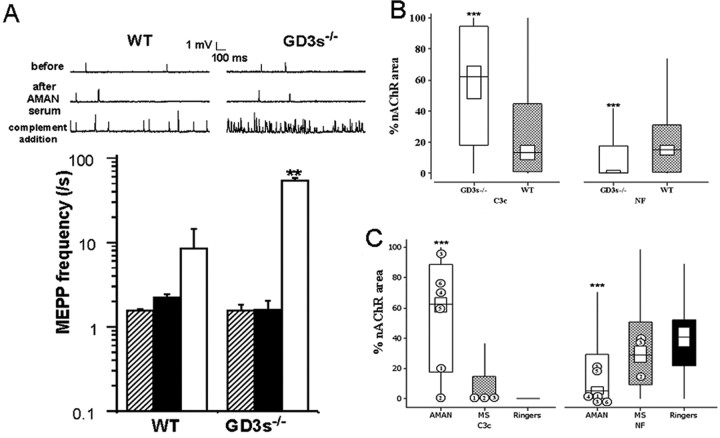
Figure 6.
Effects of human AMAN serum. Addition of AMAN serum followed by a source of complement resulted in a massive increase in asynchronous uniquantal ACh release (measured as MEPPs) at GD3s-/- diaphragm NMJs ex vivo. A, Electrophysiological recordings of MEPPs before (hatched bars) and after (black bars) complement-inactivated AMAN serum addition demonstrated that the serum alone had no effect. Subsequent addition of 40% NHS (white bar) caused a massive increase in MEPP frequency (sample traces shown). **p < 0.005 compared with WT. B, Immunohistological investigation of NMJs from these preparations revealed that GD3s-/- (white box) NMJs from AMAN serum-treated preparations had elevated levels of C3c and reduced levels of NF compared with WT (hatched box) NMJs. The median value, the interquartile range, and 1.5× the interquartile range of C3c and NF data are expressed as described in Materials and Methods. ***p < 0.001 compared with WT. C, Six human anti-GD1a-positive AMAN sera were tested for pathogenic effects using immunohistological methods in the GD3s-/- mouse as described in Materials and Methods. Parallel preparations treated with multiple sclerosis (MS) sera or Ringer's solution served as controls. Compared with both multiple sclerosis-(hatched box) or Ringer's solution-(black box) treated preparations, the AMAN sera (white box) led to elevated levels of C3c deposition and decreased levels of NF at the NMJ. The level of complement fixation varied considerably between the AMAN samples, but four of the six caused a very large reduction in NF (median of 0 for samples 1, 3, 4, and 6), whereas the other two caused a minor loss in NF.