Figure 6.
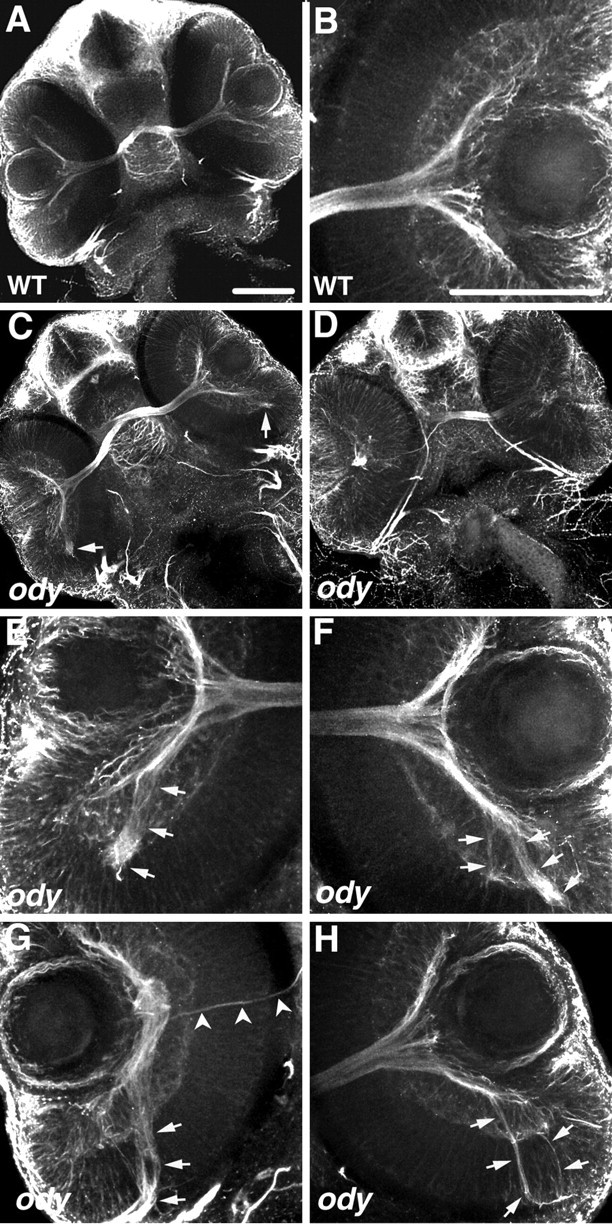
The cxcr4b mutant, odysseus (ody), displays pathfinding defects by RGC axons within the retina. All panels are confocal images of ventrally mounted 48 hpf embryos labeled with anti-acetylated α-tubulin. A, B, Retinas and optic nerves in a wild-type embryo (A) and close-up view of the retina and adjacent optic nerve (B). C-H, RGC axons in ody embryos frequently extend in aberrant directions within the retina (arrows). Retinas of embryo in C are shown under higher magnification in E and F; those of embryo in D are shown in higher magnification in G and H. Arrowheads in G indicate the axons projecting normally, exiting at the optic nerve head, whereas the majority of RGC axons project posteriorly (arrow). Scale bar, 20 μm.
