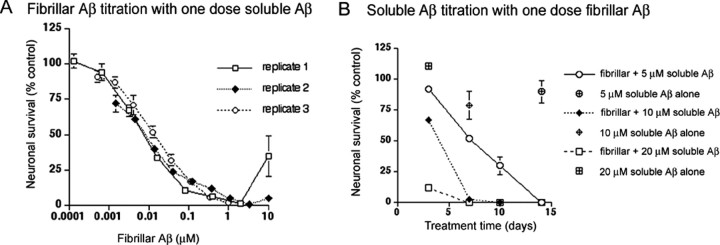
Figure 4.
The extent of Aβ-mediated neuronal cell death is dependent on both fibrillar Aβ concentration and on soluble Aβ concentration. A, Human cortical neurons were pretreated for 1 h with the indicated concentrations of fibrillar Aβ. Nonadhering fibrillar Aβ was removed by aspiration, and 20 μm soluble Aβ was added to the cultures. Neuronal cultures were incubated for 3 d and then assayed for viability using alamarBlue. Three independent neuronal culture preparations were assayed on different days using frozen aliquots of the same fibrillar Aβ preparation. We presume that the variability seen at the highest concentration of fibrillar Aβ is attributable to variations in the amount of fibrillar Aβ left behind after aspiration of the fibrillar Aβ pretreatment. Sufficiently high concentrations of fibrillar Aβ can inhibit toxicity, as seen in Figure 6, and this variability was eliminated when the fibrillar Aβ pretreatment was washed with media alone before adding soluble Aβ (data not shown). B, Human cortical neurons were pretreated for 1 h with 1 μm fibrillar Aβ. Pretreatment was aspirated, and 5 μm (circles), 10 μm (diamonds), or 20 μm (squares) soluble Aβ was added to the cultures. Neuronal viability was determined by alamarBlue after 3, 7, 10, and 14 d of treatment. All treatments were in triplicate wells. Error bars indicate ± SD.