Figure 3.
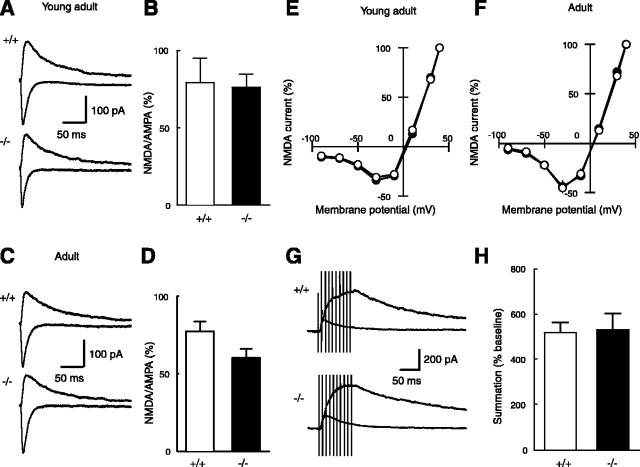
Unaltered properties of the NMDA receptor in Ptprz-deficient mice. A, Sample traces of NMDA EPSCs (upward traces; recorded at +40 mV) and AMPA EPSCs (downward traces; recorded at -90 mV) in young adult wild-type (+/+) and mutant (-/-) mice. B, The ratio of amplitudes of the NMDA EPSC to those of the AMPA EPSC was not significantly different (p > 0.8) between young adult wild-type (79.2 ± 15.7%; n = 6) and mutant (76.3 ± 8.2%; n = 8) mice. The ratio was calculated for each cell, and the values were then averaged for all cells. C, Sample traces of NMDA EPSCs and AMPA EPSCs in adult wild-type (+/+) and mutant (-/-) mice. D, The ratio of the NMDA EPSC to those of the AMPA EPSC was not significantly different (p > 0.06) between adult wild-type (77.4 ± 6.2%; n = 16) and mutant (60.3 ± 5.9%; n = 15) mice. E, The current-voltage relationships of NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs in young adult wild-type (○; n = 6) and mutant (•; n = 8) mice. Current amplitudes, which were not different between the two genotypes, were normalized to the value obtained at +40 mV for easier comparison. F, The current-voltage relationships of NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs in adult wild-type (○; n = 15) and mutant (•; n = 14) mice. G, Sample traces showing the summation of NMDA EPSCs during repetitive stimulation (100 Hz, 100 ms) in adult wild-type (+/+) and mutant (-/-) mice. The baseline EPSC evoked by a single pulse (smaller trace; average of 10 consecutive responses) is superimposed on the synaptic response evoked by 10 pulses (larger trace). H, The ratio of the amplitude of the 10th NMDA EPSC during the repetitive stimulation to that of the baseline NMDA EPSC evoked by a single pulse was not significantly different between adult wild-type (518.5 ± 44.1% of baseline; n = 7) and mutant (531.9 ± 69.6% of baseline; n = 6) mice.